George Hripcsak, Chair Of OHDSI Coordinating Center, to be Awarded Morris F. Collen Award of Excellence at AMIA 2022 Symposium
 The American College of Medical Informatics (ACMI) will present the 2022 Morris F. Collen Award of Excellence to George Hripcsak, MD, MS, FACMI, Vivian Beaumont Allen Professor and Chair of the Department of Biomedical Informatics, Columbia University, during the opening session of the American Medical Informatics Association (AMIA) 2022 Annual Symposium. AMIA’s Annual Symposium is November 5-9 in Washington, D.C.
The American College of Medical Informatics (ACMI) will present the 2022 Morris F. Collen Award of Excellence to George Hripcsak, MD, MS, FACMI, Vivian Beaumont Allen Professor and Chair of the Department of Biomedical Informatics, Columbia University, during the opening session of the American Medical Informatics Association (AMIA) 2022 Annual Symposium. AMIA’s Annual Symposium is November 5-9 in Washington, D.C.
In honor of Morris F. Collen, a thought leader in the field of medical informatics, this prestigious award is presented to an individual whose personal commitment and dedication to medical informatics has made a lasting impression on the field. The award is determined by ACMI’s Awards Committee.
“ACMI is pleased to recognize Dr. Hripcsak for his substantial accomplishments to the field of biomedical informatics,” said ACMI President Genevieve Melton-Meaux, MD, PhD, FACMI, Professor of Surgery and Health Informatics and Director of the Center for Learning Health System Sciences, University of Minnesota, Chief Analytics and Care Innovation Officer, Fairview Health Services. “Dr. Hripcsak’s contributions have stretched around the globe and his collaboration with those both inside and outside of our field has expanded the reach and impact of informatics. As a mentor, Dr. Hripcsak reminds his peers to ‘Do good work.’ I am grateful for the guidance and mentorship he has provided to me and many others in biomedical informatics.”
Collaborator Spotlight: Jing Li
 Jing Li is an Associate Director of Data Science at IQVIA, where she is leading a global team of data scientists on real world studies, focusing on treatment patterns, and drug safety studies. She has several years of industry experience in predictive modeling, machine learning, and data management, and she decided to focus her work on healthcare research in 2019.
Jing Li is an Associate Director of Data Science at IQVIA, where she is leading a global team of data scientists on real world studies, focusing on treatment patterns, and drug safety studies. She has several years of industry experience in predictive modeling, machine learning, and data management, and she decided to focus her work on healthcare research in 2019.
Jing has grown into a leader in the OHDSI Asia-Pacific (APAC) Community. She leads the bi-weekly APAC community calls and is part of the steering group for both the APAC workgroup and APAC symposium planning committee. She was also a co-author on the first ever network study published by the APAC workgroup, Analysis of Dual Combination Therapies Used in Treatment of Hypertension in a Multinational Cohort.
In our most recent edition of the Collaborator Spotlight, Jing discusses her career and how she moved into healthcare, her excitement about the growing APAC community, and plenty more.
Perseus Tool Highlighted In Clinical Registry Efforts In OHDSI Presentation
 Perseus, an open-source tool developed within the OHDSI community, combines intuitive and easy to use Web-based UI for design and implement ETL (extract, transform, and load) configuration and service for conversion the native/raw data to the OMOP Common Data Model (CDM). Additionally, Perseus has embedded tools for search in the standardized vocabularies, generates documentation for the ETL process, create the code mappings and data quality check.
Perseus, an open-source tool developed within the OHDSI community, combines intuitive and easy to use Web-based UI for design and implement ETL (extract, transform, and load) configuration and service for conversion the native/raw data to the OMOP Common Data Model (CDM). Additionally, Perseus has embedded tools for search in the standardized vocabularies, generates documentation for the ETL process, create the code mappings and data quality check.
Zachary Wang led a live demo of this tool during the Sept. 13 community call, which was focused on ‘Clinical Registry Efforts in OHDSI’. Paul Nagy, Matthew Robinson and Lee Evans also presented on this important topic, while Emily Pfaff, a leader in the National COVID Cohort Collaborative, will join a future call to discuss Distributed Machine Learning Using OMOP.
Symposium Agenda Posted; Register Now To Be Part Of OHDSI2022!
 The OHDSI Symposium will take place Oct. 14-16 at the Bethesda North Marriott Hotel and Conference Center, and the full weekend agenda has been posted. The main conference day will include a plenary session on Objective Diagnostics: A pathway to provably reliable evidence, presentations on OHDSI support for regulatory authorities, a collaborator showcase that includes 100+ posters, 17 software demos and 8 lightning talks, and a closing talk you won’t want to miss.
The OHDSI Symposium will take place Oct. 14-16 at the Bethesda North Marriott Hotel and Conference Center, and the full weekend agenda has been posted. The main conference day will include a plenary session on Objective Diagnostics: A pathway to provably reliable evidence, presentations on OHDSI support for regulatory authorities, a collaborator showcase that includes 100+ posters, 17 software demos and 8 lightning talks, and a closing talk you won’t want to miss.
The weekend will include a full-day Saturday tutorial on An Introductory Journey From Data To Evidence, as well as several workgroup activities planned throughout the weekend. The agenda includes a full list of the software demos and lightning talks; a future version will include all of the poster titles and presenters.
There will be capped totals for all sessions, so please don’t wait until the last minute to secure your spot for our highlight event of the year!
Collaborator Spotlight: Paul Nagy
 Paul Nagy, PhD, FSIIM is Associate Professor in the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Department of Radiology with a joint appointments in Medicine and the Department of Biomedical Engineering in the School of Engineering. He received his BS from Carnegie Mellon University and his PhD at the Medical College of Wisconsin. His research focus is developing biomarkers from medical imaging to enable real world reproducible evidence from observational research.
Paul Nagy, PhD, FSIIM is Associate Professor in the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Department of Radiology with a joint appointments in Medicine and the Department of Biomedical Engineering in the School of Engineering. He received his BS from Carnegie Mellon University and his PhD at the Medical College of Wisconsin. His research focus is developing biomarkers from medical imaging to enable real world reproducible evidence from observational research.
He is the director of education for the training programs in the Biomedical Informatics and Data Science section of the Department of Medicine. He leads the Observational Health and Data Science Informatics (OHDSI) efforts at Johns Hopkins as part of the Precision Medicine initiative. He is a leader in the OHDSI community, especially within the developer community. He began the Kheiron Cohort in 2022, which serves to welcome and mentor developers, and he joined Adam Black to start the open-source community workgroup this year as well.
Nagy, who is also active in several other workgroups and co-leads the Medical Imaging WG, helped lead the DevCon 2022 event, and has developed tools to track OHDSI impact in several areas. He shared some thoughts about his career, his many contributions to the OHDSI community, and plenty more in the latest Collaborator Spotlight.
New CDM Update Process Includes New Decision Tree, Clarifies How Data Model Requests Are Made, Codified
 The July 26 community call featured a session led by Clair Blacketer, Paul Nagy and Davera Gabriel on what to do when your data does not fit into the OMOP CDM.
The July 26 community call featured a session led by Clair Blacketer, Paul Nagy and Davera Gabriel on what to do when your data does not fit into the OMOP CDM.
Our community continues to expand globally, and both individuals and organizations often look for new enhancements to the CDM. There will be a new decision tree and process implemented to try and streamline this procedure and to clarify how data model requests are made and codified, and these were presented and discussed during this meeting.
The presentation can be seen here, and it includes specific use cases presented by both Nagy and Gabriel to help show how the decision tree and process happens.
All Presentations From 2022 European Symposium Are Now Available
Collaborator Spotlight: Nicole Pratt
 Nicole Pratt, a longtime collaborator with the OHDSI community, is the Deputy Director of the Quality Use of Medicines and Pharmacy Research Centre at the University of South Australia. She is a member of the Drug Utilisation Subcommittee (DUSC) of the Australian Department of Health Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee (PBAC).
Nicole Pratt, a longtime collaborator with the OHDSI community, is the Deputy Director of the Quality Use of Medicines and Pharmacy Research Centre at the University of South Australia. She is a member of the Drug Utilisation Subcommittee (DUSC) of the Australian Department of Health Pharmaceutical Benefits Advisory Committee (PBAC).
She has a particular interest in new statistical methodologies to study the effectiveness and safety of medicine use and in the development of tools for post-marketing surveillance of medicines. This interest helped lead her to be a collaborator within the OHDSI LEGEND initiative; the LEGEND hypertension study led to a 2019 Lancet publication that found that the most popular hypertension drug wasn’t the most effective.
Nicole has also been one of the leaders in the growing Asia-Pacific (APAC) OHDSI community and the leader of the Australia chapter. She discusses her own research, the developments in the OHDSI APAC community, the importance of large community initiatives and much more in the latest edition of the Collaborator Spotlight.
Network Study Leads Share Updates, Calls For Collaboration During May 2022 Community Call
 Six OHDSI network studies were presented during a May 2022 community call to both inform the community about global research efforts (either ongoing or recently completed), as well as call for collaborators to join in these important research projects.
Six OHDSI network studies were presented during a May 2022 community call to both inform the community about global research efforts (either ongoing or recently completed), as well as call for collaborators to join in these important research projects.
These brief updates were recorded and posted to the OHDSI YouTube channel, and all presentations are available here. You can also access slides above each of the video presentations.
If you are interested in collaborating, please reach out to the presenter on Teams or within the OHDSI forums.
DARWIN EU Initiative — How OHDSI Can Collaborate With Erasmus MC and the EMA to Assist in Delivering Real-World Evidence & Supporting Regulatory Decision-Making Across Europe
Collaborator Spotlight: Asieh Golozar
 Asieh Golozar, a longtime OHDSI collaborator and the 2021 Titan Award for Clinical Application recipient, is Vice President and Global Head of Data Science at Odysseus Data Services, Inc. She also serves as Professor of the Practice & Director of Clinical Research at the OHDSI Center, Northeastern University.
Asieh Golozar, a longtime OHDSI collaborator and the 2021 Titan Award for Clinical Application recipient, is Vice President and Global Head of Data Science at Odysseus Data Services, Inc. She also serves as Professor of the Practice & Director of Clinical Research at the OHDSI Center, Northeastern University.
Golozar currently leads the Oncology workgroup, and she discusses its impact on her OHDSI journey, as well as its goals for the upcoming year. She also discusses her path to epidemiology (which wasn’t her first career path), why she is working with the Roux Institute around reproducibility, and plenty more in the latest Collaborator Spotlight.
OHDSI Launches Three-Tiered Sponsorship Program To Strengthen Foundation For Global Community Growth
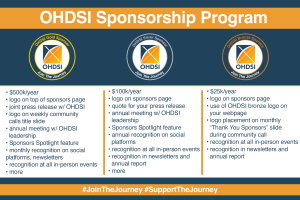 The OHDSI Coordinating Center, located in the Columbia University Department of Biomedical Informatics, supports the OHDSI open-source community and the shared mission to improve health by empowering a community to collaboratively generate the evidence that promotes better health decisions and better care. Among the ways that the Coordinating Center provides this support is through stewardship of open-community data standards, by enabling open-source development, by facilitating methods research and clinical applications, by encouraging open sharing and evidence dissemination, and by fostering collaborations and empowering a sense of community.
The OHDSI Coordinating Center, located in the Columbia University Department of Biomedical Informatics, supports the OHDSI open-source community and the shared mission to improve health by empowering a community to collaboratively generate the evidence that promotes better health decisions and better care. Among the ways that the Coordinating Center provides this support is through stewardship of open-community data standards, by enabling open-source development, by facilitating methods research and clinical applications, by encouraging open sharing and evidence dissemination, and by fostering collaborations and empowering a sense of community.
OHDSI has introduced a Sponsorship Program, which will allow both corporations and individuals to make meaningful contributions in support of OHDSI’s central coordinating activities. There are three levels of support, including donation amount and benefits to the sponsor, which are detailed on the sponsorship page.
George Hripcsak, Chair and Vivian Beaumont Allen Professor of Biomedical Informatics at Columbia University, provided a detailed presentation on the support provided by the Coordinating Center during an April 2022 community call. That presentation is available here.
Reproducibility In The OHDSI Environment — Why It Matters, And How We Improve Upon It
 The March 29 OHDSI Community Call focused on reproducibility, and three leaders in the community shared presentations on this topic. Anna Ostropolets, a PhD student at Columbia University, shared a presentation on the OHDSI Reproducibility Challenge, a one-day event held during the 2021 OHDSI Symposium that attempted to have teams of OHDSI collaborators reproduce the cohort logic for target, comparator and outcome cohorts for a published study run outside of OHDSI.
The March 29 OHDSI Community Call focused on reproducibility, and three leaders in the community shared presentations on this topic. Anna Ostropolets, a PhD student at Columbia University, shared a presentation on the OHDSI Reproducibility Challenge, a one-day event held during the 2021 OHDSI Symposium that attempted to have teams of OHDSI collaborators reproduce the cohort logic for target, comparator and outcome cohorts for a published study run outside of OHDSI.
Martijn Schuemie, a Research Fellow in epidemiology analytics at Janssen Research and Development, shared a presentation on creating reproducible studies using OHDSI tools and best practices. Topics included the need for analyses to be repeatable, writing studies as a pipeline, and how to create the proper study package.
Asieh Golozar, Vice President and Global Head of Data Science at Odysseus Data Services, Inc., shared a community update on the OHDSI Reproducibility Service, which is centered at The Roux Institute at Northeastern University. This talk includes discussion of what type of study makes for a good candidate for reproducibility, the approach with the Center, and a proof of concept study that is seeking data partner collaboration.
Videos and slides from the presentation are included within the reproducibility session homepage.
OHDSI Hosts DevCon 2022 April 22 To Welcome & Mentor New Contributors To Our Open-Source Environment
 The Open-Source Community is hosting the first Dev Con on Friday, April 22 (8 am – 12 pm ET) as a way of accepting and mentoring new contributors to our environment. Organized by Paul Nagy and Adam Black, the event will include multiple workshops, talks and a panel discussion to both welcome and engage both current and future developers within OHDSI.
The Open-Source Community is hosting the first Dev Con on Friday, April 22 (8 am – 12 pm ET) as a way of accepting and mentoring new contributors to our environment. Organized by Paul Nagy and Adam Black, the event will include multiple workshops, talks and a panel discussion to both welcome and engage both current and future developers within OHDSI.
Who should consider registering for DevCon? We are looking for people who are interested in participating with an OHDSI project team, seeing ‘under the hood’ of the OHDSI engine, or being mentored by professional developers.
The full agenda, including all eight current workshop offerings and the planned panel discussion, as well as registration links are available on our DevCon homepage.
OHDSI2022 Symposium Registration Opens For Friday Main Conference, Saturday Tutorial
 We are thrilled to announce that registration for the 2022 OHDSI Symposium, which will be held Oct. 14-16 at the Bethesda North Marriott Hotel & Conference Center, is now open!
We are thrilled to announce that registration for the 2022 OHDSI Symposium, which will be held Oct. 14-16 at the Bethesda North Marriott Hotel & Conference Center, is now open!
The main conference will be held Friday, Oct. 14, while a full-day tutorial will be held Saturday, Oct. 15. Other community activities, mainly focused on OHDSI workgroups, will be held both Oct. 15 and Oct. 16. The OHDSI2022 homepage has more information, as well as registration links to both the conference and the tutorial (these are separate events and each requires its own registration), information on the collaborator showcase, hotel room blocks, and plenty more.
Direct registration is available for both the main conference and the full-day tutorial. Please continue to check our symposium homepage and our social platforms, and join the weekly OHDSI community calls, for more information.
Standardized Vocabularies Presentation Highlights Development And Community Impact, Looks To Future Growth
 The March 22 OHDSI Community Call provided an in-depth look at the OHDSI vocabulary, from how it is developed, to how it can be utilized, and where it should grow from here. Three leaders from the vocabulary workgroup joined to present a trio of topics for this session (see below), and the video is now available along with the Standardized Vocabulary introduction from the book of OHDSI.
The March 22 OHDSI Community Call provided an in-depth look at the OHDSI vocabulary, from how it is developed, to how it can be utilized, and where it should grow from here. Three leaders from the vocabulary workgroup joined to present a trio of topics for this session (see below), and the video is now available along with the Standardized Vocabulary introduction from the book of OHDSI.
Michael Kallfelz (Physician Executive • Odysseus Data Services) led a discussion on “A peek into the OHDSI vocabulary engine room,” while Patrick Ryan (Vice President, Observational Health Data Analytics • Janssen Research & Development) provided a presentation on “Fun things you can learn with the OHDSI standardized vocabularies.” Christian Reich (Vice President, RWE Systems • IQVIA) concluded the presentation with a forward-looking discussion: “Time for reflection • Where are we? Where should we be?”
This session also introduced as to members of the OHDSI vocabulary team and all the work it takes to create the OHDSI vocabularies, which are critical for the success of our community. The slides from this presentation are available here.
Common Data Model Team Leads CDM 5.4 Workshop; Full Video Tutorial Is Now Available
Collaborator Spotlight: Maxim Moinat
 Maxim Moinat is a data engineer with a demonstrated history of working in bioinformatics and medical informatics. He has worked as a data engineer/software developer for The Hyve since 2016, and recently became a scientific researcher for the Erasmus MC medical informatics department. He has been a long-time collaborator with both the OHDSI and EHDEN communities.
Maxim Moinat is a data engineer with a demonstrated history of working in bioinformatics and medical informatics. He has worked as a data engineer/software developer for The Hyve since 2016, and recently became a scientific researcher for the Erasmus MC medical informatics department. He has been a long-time collaborator with both the OHDSI and EHDEN communities.
Maxim earned a 2021 Titan Award honoree for his invaluable contributions in data standards. He leads the Registry workgroup, contributes to open-source development and has provided tutorials and other presentations during global community calls. He said his passion is to apply his skills to advance biomedical science, ultimately improving healthcare for many patients.
Maxim recently shared several insights in our latest Collaborator Spotlight.
European Medicines Agency Announces OHDSI Collaborator Erasmus University Will Initiate DARWIN EU Coordination Center
 The European Medicines Agency (EMA) announced Feb. 9 that Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam has been contracted to establish the DARWIN EU (Data Analysis and Real World Interrogation Network) Coordination Centre.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) announced Feb. 9 that Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam has been contracted to establish the DARWIN EU (Data Analysis and Real World Interrogation Network) Coordination Centre.
The role of the Coordination Centre is to develop and manage a network of real-world healthcare data sources across the EU and to conduct scientific studies requested by medicines regulators and, at a later stage, requested by other stakeholders.
The vision of DARWIN EU is to give EMA and national competent authorities in EU Member States access to valid and trustworthy real-world evidence, for example on diseases, patient populations, and the use, safety and effectiveness of medicines, including vaccines, throughout the lifecycle of a medicinal product.
Peter Rijnbeek, a veteran OHDSI collaborator and Titan Award honoree, is the Chair of the Department of Medical Informatics of the Erasmus Medical Center.
COVER Prediction Model Generated During COVID Study-A-Thon Published; Lead Authors Share Thoughts On Model, Impact
 The first COVID-19 prediction model developed and validated by the OHDSI community following the March 2020 global study-a-thon was recently published by BMC Medical Research Methodology.
The first COVID-19 prediction model developed and validated by the OHDSI community following the March 2020 global study-a-thon was recently published by BMC Medical Research Methodology.
The study “Seek COVER: using a disease proxy to rapidly develop and validate a personalized risk calculator for COVID-19 outcomes in an international network” developed COVID-19 Estimated Risk (COVER) scores that quantify a patient’s risk of hospital admission with pneumonia (COVER-H), hospitalization with pneumonia requiring intensive services or death (COVER-I), or fatality (COVER-F) in the 30-days following COVID-19 diagnosis using historical data from patients with influenza or flu-like symptoms and tested this in COVID-19 patients.
Led by co-first authors Ross Williams and Aniek Markus, both of whom share thoughts on both the model and its impact in this writeup, the team designed a nine-predictor risk model that was validated using more than 44,500 COVID patients (following initial development and validation using more than 6.8 million patients with influenza or flu-like symptoms). This model predicts hospitalization, intensive services, and death, and can help provide reassurance for low-risk patients, while shielding high-risk patients, as many start to enter the de-confinement stage of the pandemic.
Phenotype Phebruary: Stay Involved With The Daily Conversations Around Phenotype Development And Evaluations
 “Phenotype Phebruary” is a community-wide initiative to both develop and evaluate phenotypes for health outcomes that could be investigated by the community. Patrick Ryan introduced this initiative in both a video presentation and a forum post, and each of the conversations around the “28 phenotypes for 28 days” are being held within the OHDSI forums.
“Phenotype Phebruary” is a community-wide initiative to both develop and evaluate phenotypes for health outcomes that could be investigated by the community. Patrick Ryan introduced this initiative in both a video presentation and a forum post, and each of the conversations around the “28 phenotypes for 28 days” are being held within the OHDSI forums.
Our Phenotype Phebruary homepage will provide direct links to each forum post, which is where conversations around each specific phenotype should be held. Please be active in these discussions. There are many ways you can contribute, including joining the conversation, evaluating the cohort definitions in your own data (execute cohort definitions and CohortDiagnostics in your CDM, hare insights you learn from your data on the forums, etc.), or lead your own discussions on phenotypes of interest.
N3C Leadership Presents Work On Extracting OHDSI Concepts from Clinical Narratives for COVID
 Hongfang Liu (Mayo Clinic) and Christopher Chute (Johns Hopkins University) led a session on Extracting OHDSI Concepts from Clinical Narratives for COVID during the Jan. 25 OHDSI Community Call. Following the presentation (approximately 33 minutes), there was a Q&A session.
Hongfang Liu (Mayo Clinic) and Christopher Chute (Johns Hopkins University) led a session on Extracting OHDSI Concepts from Clinical Narratives for COVID during the Jan. 25 OHDSI Community Call. Following the presentation (approximately 33 minutes), there was a Q&A session.
Following an overview of the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C), the presentation focused on Open Health Natural Language Processing and collaborating with the NLP-empowered RECOVER work.
You can watch the full video here, and you can access the slides here.
Vaccine Surveillance Method in Observational Data May Generate High Number Of False Positives
 Worldwide efforts to promote vaccination require reliable evidence about the safety and effectiveness of vaccines to build trust in their use. Regulators and other public health agencies play a critical role in generating and synthesizing evidence across an array of data sources as part of a collective public health infrastructure.
Worldwide efforts to promote vaccination require reliable evidence about the safety and effectiveness of vaccines to build trust in their use. Regulators and other public health agencies play a critical role in generating and synthesizing evidence across an array of data sources as part of a collective public health infrastructure.
One desired component of that system is the use of observational data, such as de-identified electronic health records and administrative claims, to conduct analyses that can identify true adverse events of vaccines as quickly as possible, while simultaneously reducing the chance that analyses generate false positive findings that may stimulate unnecessary worry.
In this context, understanding the reliability of study designs in vaccine surveillance systems is important to ensure that evidence is appropriately used by all stakeholders.
Historical comparator designs, which compare background rates of events in a general population versus observed rates amongst a vaccinated cohort, have been regularly used by regulators and other vaccine safety researchers. Those studies may generate a high number of false positives, according to a recent study published in Frontiers in Pharmacology. The paper, which studied the methods used for surveillance of the H1N1, flu, and other recent vaccines, highlight a need to further evaluate study design in this critical time of COVID-19 vaccine surveillance.
Age-sex adjustment and empirical calibration were among the measures used to produce more reliable surveillance monitoring findings, according to the study “Bias, Precision and Timeliness of Historical (Background) Rate Comparison Methods for Vaccine Safety Monitoring: An Empirical Multi-Database Analysis” led by Xintong Li, a DPhil candidate at the University of Oxford, and supported by the OHDSI and EHDEN open science communities
Our Journey: New Publication Highlighting All Aspects Of OHDSI’s Global Community, Released At #OHDSI2021, Is Available To Global Community
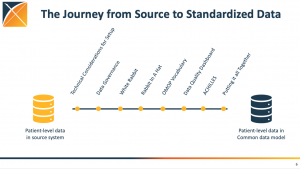
 Our Journey: Where The OHDSI Community Came From, And Where We Are Going, a new publication released at the 2021 OHDSI Global Symposium, is available for download to the global community. This publication highlights all aspects of the global community, ranging from its start and global mission, to its OMOP Common Data Model and global data network, to its collaborative efforts, ranging from study-a-thons and symposia to a full list of more than 360 community publications.
Our Journey: Where The OHDSI Community Came From, And Where We Are Going, a new publication released at the 2021 OHDSI Global Symposium, is available for download to the global community. This publication highlights all aspects of the global community, ranging from its start and global mission, to its OMOP Common Data Model and global data network, to its collaborative efforts, ranging from study-a-thons and symposia to a full list of more than 360 community publications.
The book is divided into 9 chapters (see the graphic to the right), including sections on collaborators and collaborative activities, data standards, methods research, and open-source software. The history of OHDSI publications, including a graphic to show just how collaborative the community is, and our work around COVID-19 is also included, as is a look at future goals for the OHDSI community.
While the download is free, you are able to order the book for yourself, or for your organization. Please reach out to clientservices@abgprint.com for more information.
Ongoing Network Studies, Calls For Collaboration, Highlighted During November Community Call
 Six OHDSI network studies, ranging from those in development to those nearing completion, were presented during the Nov. 16 community call, the second open studies call of 2021. The calls highlighted the breadth of research happening in the community, but also served as calls for collaboration on these important efforts. The individual study presentations are available at the links below.
Six OHDSI network studies, ranging from those in development to those nearing completion, were presented during the Nov. 16 community call, the second open studies call of 2021. The calls highlighted the breadth of research happening in the community, but also served as calls for collaboration on these important efforts. The individual study presentations are available at the links below.
-
-
- Asieh Golozar: Prognostic Significance of Liver Metastasis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Leena Elhussein: Redefining Polypharmacy: A Longitudinal Study in Routinely Collected Data
- Noémie Elhadad: Health Equity Research Assessment (HERA) Characterization
- Jacob Zelko: Assessing Health Equity in Mental Healthcare Delivery Using a Federated Network Research Model
- Annika Jodicke and Kristin Kostka: Long COVID Phenotyping and Vaccine Effectiveness Methods
- Erica Voss: Adverse Events of Special Interest within COVID-19 Subjects
-
The LEGEND Initiative — From Its Development And Impact On Hypertension To Future Research Plans Around Type 2 Diabetes
 The LEGEND (Large-scale Evidence Generation and Evaluation across a Network of Databases) Initiative applies high-level analytics to perform observational research on hundreds of millions of patient records within OHDSI’s international database network.
The LEGEND (Large-scale Evidence Generation and Evaluation across a Network of Databases) Initiative applies high-level analytics to perform observational research on hundreds of millions of patient records within OHDSI’s international database network.
LEGEND principles have been applied to studying the effects of treatments for depression, hypertension, and COVID-19, and are being applied to Type 2 diabetes. The clinical impact of LEGEND has already been observed, with important evidence that promotes better health decisions published in Lancet, JAMA Internal Medicine, and Hypertension.
During the Oct. 19 OHDSI Community Call, members of the LEGEND team provided a comprehensive presentation around this initiative, its work around hypertension, and plans around Type 2 diabetes.
Plenaries, Panels, Posters and More! The 2021 OHDSI Global Symposium Home Page Includes All Materials From the Two Main Days
 The 2021 OHDSI Global Symposium featured plenary presentations on both OHDSI’s Impact on the COVID-19 Pandemic, as well as on the Journey to Reliable Evidence. The main days included the State of the Community Presentation, the Collaborator Showcase, and a memorable Closing Ceremony that focused on OHDSI’s work through the perspective of a patient.
The 2021 OHDSI Global Symposium featured plenary presentations on both OHDSI’s Impact on the COVID-19 Pandemic, as well as on the Journey to Reliable Evidence. The main days included the State of the Community Presentation, the Collaborator Showcase, and a memorable Closing Ceremony that focused on OHDSI’s work through the perspective of a patient.
There were also a pair of activities, including the first OHDSI Reproducibility Challenge workshop, and a full-day tutorial on building conceptsets.
All materials from the 2021 Symposium will be shared on this page in the coming weeks. The first two sessions, as well as links to the collaborator showcase presentations, are currently available below.
OHDSI2021 Is On!
 The 2021 OHDSI Symposium began Sunday, Sept. 12, with a full-day tutorial on Building Conceptsets, and then completed its first reproducibility challenge workshop (see image, right). Finally, the main two days began with the first of two plenaries, focusing on OHDSI’s impact on the COVID-19 pandemic. It concludes Wednesday with a plenary focusing on the journey to reliable evidence.
The 2021 OHDSI Symposium began Sunday, Sept. 12, with a full-day tutorial on Building Conceptsets, and then completed its first reproducibility challenge workshop (see image, right). Finally, the main two days began with the first of two plenaries, focusing on OHDSI’s impact on the COVID-19 pandemic. It concludes Wednesday with a plenary focusing on the journey to reliable evidence.
Recordings from all sessions will be posted in the near future, including both reaction panels, which brought together leaders in the field to comment on what they learned from OHDSI presentations. Please continue to check OHDSI.org and our social feeds for an announcement on when those videos will be available.
Daily Agenda For 2021 OHDSI Global Symposium Unveiled, Includes 2 Plenaries, Workshop, Tutorial and Interactive Collaborator Showcase
The daily agenda for the  2021 OHDSI Global Symposium, set for Sept. 12-15, includes a pair of plenaries (Sept. 14: OHDSI Impact on the COVID-19 Pandemic; Sept. 15: Generating Reliable Evidence), the first-ever OHDSI Reproducibility Challenge, a full-day tutorial on Building Conceptsets, and an interactive Collaborator Showcase that will have sessions convenient for collaborators around the world.
2021 OHDSI Global Symposium, set for Sept. 12-15, includes a pair of plenaries (Sept. 14: OHDSI Impact on the COVID-19 Pandemic; Sept. 15: Generating Reliable Evidence), the first-ever OHDSI Reproducibility Challenge, a full-day tutorial on Building Conceptsets, and an interactive Collaborator Showcase that will have sessions convenient for collaborators around the world.
The Symposium, which will be held in the OHDSI MSTeams environment, will begin Sunday, Sept. 12, with the Building Conceptsets tutorial, and then will continue on Monday with the OHDSI Reproducibility Challenge. The traditional symposium will take place over Sept. 14-15, with plenaries and collaborator showcase sessions on both days.
Check out the symposium homepage for more information, and for all registration links.
Community-Led ETL, CDM Sessions Highlight Impact Of Focused Activities Within OHDSI
 Mui Van Zandt and Clair Blacketer, a pair of Titan Award honorees within OHDSI, led a pair of community-driven activities that had multiple benefits during August.
Mui Van Zandt and Clair Blacketer, a pair of Titan Award honorees within OHDSI, led a pair of community-driven activities that had multiple benefits during August.
Van Zandt, a leader in the Asia-Pacific (APAC) community, ran a two-day ETL tutorial August 12-13 that featured seven different sessions (Introduction to ETL & Source Data Analysis, Vocabulary Mapping Part I, Vocabulary Mapping Part II, ETL Specification Writing, ETL Specification Review, Common Issues in ETL Conversion and OMOP ETL Development, and Data Quality Checks). You can watch all of the recordings now on the tutorial homepage.
Blacketer led a two-day CDM Hackathon August 18-19 that welcomed 25 collaborators (see screenshot, right) and focused on our data standards in the OMOP common data model. The team addressed 33 issues, closed 30 pull requests and ended with a fully-functional R package. This effort was devoted to the preparation for OMOP CDM v5.4 and included work on documentation. You can hear about both activities during the Aug. 24 OHDSI Community Call.
HADES Unit-Test-A-Thon Aids Reliability Of Open-Source Tool Packages That Drive Community Research
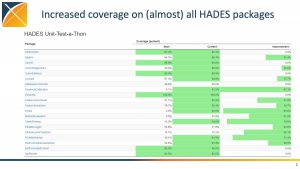 When Martijn Schuemie planned a HADES (Health Analytics Data to Evidence Suite) Unit-Test-A-Thon, his goal was to improve some HADES packages to greater than 80% coverage, and to familiarize more community members with the code and these tools.
When Martijn Schuemie planned a HADES (Health Analytics Data to Evidence Suite) Unit-Test-A-Thon, his goal was to improve some HADES packages to greater than 80% coverage, and to familiarize more community members with the code and these tools.
He didn’t necessarily expect a wide swath of the community to come together for one of OHDSI’s most successful collaborative events in 2021, but he was happy to see such a successful community event. 32 collaborators — ranging from veteran to newcomer — came together to significantly enhance the community-developed tool package that serves as the foundation for almost all community research.
Three collaborators presented about both the event and what they learned from it during a recent community call.
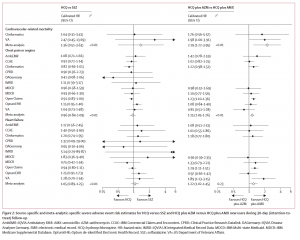
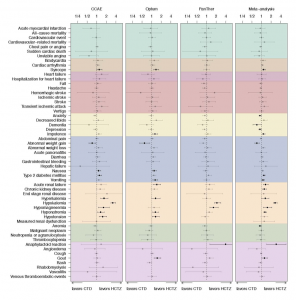
Among Effective Antihypertensive Drugs, Less Popular Choice Is Slightly Safer
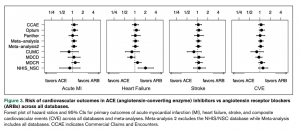 Two types of drugs that are recommended as a first treatment for patients with high blood pressure were found equally effective in improving cardiovascular outcomes, though the more popular type causes slightly more side effects, finds a multinational observational study led by researchers within the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) community.
Two types of drugs that are recommended as a first treatment for patients with high blood pressure were found equally effective in improving cardiovascular outcomes, though the more popular type causes slightly more side effects, finds a multinational observational study led by researchers within the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) community.
The study, which analyzed claims and electronic health data from millions of patients worldwide, is the largest to compare the safety and efficacy of ACE inhibitors and ARBs, two commonly prescribed antihypertensive drugs. It was published online in Hypertension on July 26, 2021.
“Physicians in the United States and Europe overwhelmingly prescribe ACE inhibitors, simply because the drugs have been around longer and tend to be less expensive than ARBs,” says George Hripcsak, MD, Vivian Beaumont Allen Professor and chair of biomedical informatics at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and senior author of the study. Columbia University serves as the coordinating center for the OHDSI community.
“But our study shows that ARBs are associated with fewer side effects than ACE inhibitors. The study was focused on first-time users of these drugs. If you’re just starting drug therapy for hypertension, you might consider trying an ARB first. If you’re already taking an ACE inhibitor and you’re not having any side effects, there is nothing that we found that would indicate a need for a change.”
Design & Preliminary Findings From PROTEUS Study, Generated At #OHDSI2020, Shared With OHDSI Community
 The PROTEUS (Predicting & Recalibrating Outcomes Toward External Understanding Study) study was presented during our July 13 Community Call.
The PROTEUS (Predicting & Recalibrating Outcomes Toward External Understanding Study) study was presented during our July 13 Community Call.
The foundation of this study took place during the 2020 OHDSI Global Symposium. The presentation was led by the two study leaders, David Kent (Professor of Medicine, Clinical & Translational Science Tufts Medical Center) and Benjamin Wessler (Director, Valve Center; Assistant Professor, Tufts University School of Medicine).
Both the video presentation and slides are available for the community.
EUMAEUS Team Presents OHDSI Study On Evaluating Use of Methods for Adverse Event Under Surveillance
 As approved COVID-19 vaccines are rolled out globally, it is likely that safety signals will be identified from spontaneous reports and other data sources. Although some work has been done on the best methods for vaccine safety surveillance, there is a scarcity of information on how these perform in analyses of real-world data. The EUMAEUS (Evaluating Use of Methods for Adverse Event Under Surveillance) team is collaborating to study the comparative performance (bias, precision, and timeliness) of different analytical methods for the study of comparative vaccine safety.
As approved COVID-19 vaccines are rolled out globally, it is likely that safety signals will be identified from spontaneous reports and other data sources. Although some work has been done on the best methods for vaccine safety surveillance, there is a scarcity of information on how these perform in analyses of real-world data. The EUMAEUS (Evaluating Use of Methods for Adverse Event Under Surveillance) team is collaborating to study the comparative performance (bias, precision, and timeliness) of different analytical methods for the study of comparative vaccine safety.
This work was presented during a June community call (video presentation and slides are available). The topics for the presentation are listed below.
-
-
- Literature Review (Lana Lai, Postdoctoral Research Associate, University of Manchester)
- Overview of the EUMAEUS Experiment Design (Marc Suchard, Professor, Department of Biomathematics, UCLA)
- Bias, Precision and Timeliness of Historical Rate Comparison Methods (Xintong Li, DPhil Candidate, University of Oxford)
- Combining Methods in a Safety Surveillance System (Faaizah Arshad, Undergraduate, UCLA)
- Estimating for Two-Dose Vaccines (Ty Stanford, Data Analyst/Bioinformatician, University of South Australia)
- Comparison of Performance Across Methods (Martijn Schuemie, Research Fellow, Epidemiology Analytics, Janssen Research and Development)
-
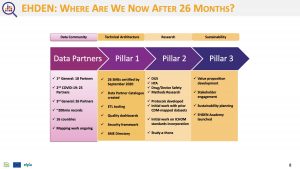
EHDEN Welcomes 41 New Data Partners Representing 78 Million Patient Records, Brings In Seven New Nations And 12 Focused On Oncology
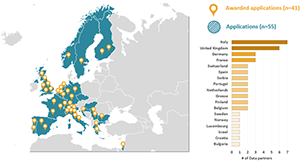 Our colleagues within the EHDEN Consortium recently announced a total of 41 data partners have been selected in our latest open call for data partners. These 41 applications, which came from 55 eligible applications, were selected by the EHDEN Data Source Prioritisation Committee. Combined, the 41 selected data partners represent over 78 million patient records, originating from various care settings.
Our colleagues within the EHDEN Consortium recently announced a total of 41 data partners have been selected in our latest open call for data partners. These 41 applications, which came from 55 eligible applications, were selected by the EHDEN Data Source Prioritisation Committee. Combined, the 41 selected data partners represent over 78 million patient records, originating from various care settings.
This open call had a focus on countries minimally represented in the current EHDEN network, and with this current call, we now have data partners in 7 new countries: Greece, Bulgaria, Israel, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland and Luxembourg. Secondly, the oncology focus was a huge success with 12 new data partners having a focus on oncology while we also welcome several new data partners with a focus on Diabetes Mellitus. EHDEN looks forward to all the new Data Partners joining with the 60 Data Partners across the 16 countries from our prior three calls.
Following the harmonization process, the EHDEN data network will have 98 total data partners across 22 nations.
Largest, Most Extensive Measurement Of Adverse Events Background Rates Can Inform Safety Monitoring Efforts For COVID Vaccines
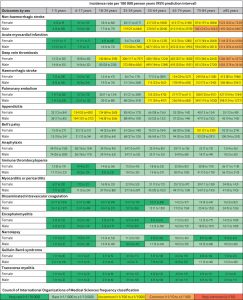 COVID vaccine surveillance efforts are a global priority, but safety monitoring for vaccines should not reflect a single global population. The largest international network study ever completed on the background rates of adverse events of special interest (AESI) being monitored in vaccine surveillance efforts identified that these rates vary substantially by age, sex, and database.
COVID vaccine surveillance efforts are a global priority, but safety monitoring for vaccines should not reflect a single global population. The largest international network study ever completed on the background rates of adverse events of special interest (AESI) being monitored in vaccine surveillance efforts identified that these rates vary substantially by age, sex, and database.
Led by researchers at Oxford University, Columbia University, Erasmus MC, UCLA, and Janssen, an international team of collaborators within the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) network provided a timely reference of the background rates of AESIs in the recent study “Characterising the background incidence rates of adverse events of special interest for covid-19 vaccines in eight countries: multinational network cohort study” published June 14 by The BMJ.
There were significant differences in the observed rates of AESIs based on the age groups and sex of more than 126 million people across four continents and 13 total databases in this observational study. Furthermore, differences were observed across people in distinct databases.
COVID-19 Shows Greater Complications In Youth Than Influenza, Though Fatality Is Rare
 While fatality was fortunately rare, complications including hospitalization, hypoxemia and pneumonia were more frequent in children and adolescents either diagnosed or hospitalized with COVID-19 than with seasonal influenza. Furthermore, labored breathing, loss of smell and gastrointestinal issues were more prevalent symptoms for younger people inflicted with COVID-19 than with influenza.
While fatality was fortunately rare, complications including hospitalization, hypoxemia and pneumonia were more frequent in children and adolescents either diagnosed or hospitalized with COVID-19 than with seasonal influenza. Furthermore, labored breathing, loss of smell and gastrointestinal issues were more prevalent symptoms for younger people inflicted with COVID-19 than with influenza.
These findings, along with that of significant treatment heterogeneity for children/adolescents hospitalized with COVID-19, were presented in the study “30-day outcomes of Children and Adolescents with COVID-19: An International Experience,” published May 28 by Pediatrics.
Early in the pandemic, opinions around the COVID-19 impact on children and adolescents ranged from it being no more than the common flu to fear of its potential impact on lesser-developed immune systems. This OHDSI global network study compared the real-world observational data of more than 242,000 children/adolescents diagnosed and nearly 10,000 hospitalized with COVID-19 to more than 2,000,000 diagnosed with influenza across five countries (France, Germany, South Korea, Spain, United States) to provide a clearer picture of its impact.
PIONEER Prostate Cancer Study-A-Thon Report Provided During May Community Call
 Collaborators from PIONEER, EHDEN and OHDSI came together during a five-day stretch in March to investigate the natural history and outcomes of prostate cancer patients managed with watchful waiting, a conservative management option for prostate cancer patients with a life expectancy of less than 10 years at time of diagnosis. The patient’s disease is ‘watched’ for development of local or systemic progression until they require palliative treatment (care that makes a disease or its symptoms less severe or unpleasant but without removing the cause), with the intention being to maintain quality of life.
Collaborators from PIONEER, EHDEN and OHDSI came together during a five-day stretch in March to investigate the natural history and outcomes of prostate cancer patients managed with watchful waiting, a conservative management option for prostate cancer patients with a life expectancy of less than 10 years at time of diagnosis. The patient’s disease is ‘watched’ for development of local or systemic progression until they require palliative treatment (care that makes a disease or its symptoms less severe or unpleasant but without removing the cause), with the intention being to maintain quality of life.
The aim of this study-a-thon was to assess selection criteria and long-term outcomes of prostate cancer patients on watchful waiting by using an international network of real-world data spanning the years watchful waiting has been a recognized prostate cancer management approach.
Output from that study-a-th0n, as well as ongoing work in this important research topic, was shared in this presentation.
Six Asia-Pacific Regional Chapters Provide Exciting Updates, Share Upcoming Goals, During Recent APAC Call
 Many of the exciting advancements within our global OHDSI community were presented recently at an Asia-Pacific (APAC) community call, when representatives from the six different APAC regional chapters (Australia, China, Japan, Korea, Singapore and Taiwan) provided updates on both their recent accomplishments and upcoming missions.
Many of the exciting advancements within our global OHDSI community were presented recently at an Asia-Pacific (APAC) community call, when representatives from the six different APAC regional chapters (Australia, China, Japan, Korea, Singapore and Taiwan) provided updates on both their recent accomplishments and upcoming missions.
The recording of that call is available here, while a summary can be found within this story.
The APAC community call takes place every other week within our MS Teams environment, and the recordings our posted to our APAC Community homepage. Information for how to join the calls, or any of our regional chapters, are available on that page.
Insufficient Data, Misleading Recommendations Led To Significant Early Heterogeneity In Global COVID-19 Patient Management
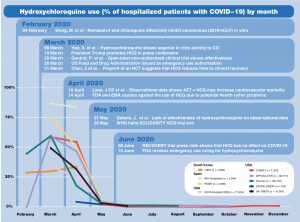 While there was extensive use of drug repurposing throughout the first 10 months of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was substantial heterogeneity over the types of drugs used for treatment purposes globally. Some drugs, including hydroxychloroquine, saw sharp declines in use, while adjunctive therapies grew into a more relied upon method for patient management.
While there was extensive use of drug repurposing throughout the first 10 months of the COVID-19 pandemic, there was substantial heterogeneity over the types of drugs used for treatment purposes globally. Some drugs, including hydroxychloroquine, saw sharp declines in use, while adjunctive therapies grew into a more relied upon method for patient management.
In a number of cases, scientific discovery overturned misconceptions proclaimed via press conferences and social media.
The OHDSI network study “Use of repurposed and adjuvant drugs in hospital patients with covid-19: multinational network cohort study,” published May 11 by The BMJ, provides a global view of drug utilization in routine practice of more than 303,000 hospitalized patients from China, South Korea, Spain and the United States. The study highlights the need for future research on the safety and efficacy of the more commonly used treatments.
Collaborator Spotlight: Evan Minty
 Evan Minty is a general internist and clinical assistant professor at the O’Brien Institute for Public Health at the University of Calgary, Canada. He splits his time between clinical practice, applied clinical informatics with Alberta Health Services (supporting their EMR deployments and decision support development) and research interests in clinical and EMR data science.
Evan Minty is a general internist and clinical assistant professor at the O’Brien Institute for Public Health at the University of Calgary, Canada. He splits his time between clinical practice, applied clinical informatics with Alberta Health Services (supporting their EMR deployments and decision support development) and research interests in clinical and EMR data science.
Evan completed his undergraduate degree in Biophysics at the University of British Columbia, his MSc in Physics at the University of Alberta, his MD and General Internal Medicine residency and fellowship training at the University of Calgary, and his MSc in Biomedical Informatics through Stanford University. He remains onboarded through Stanford University as a research affiliate. He is an active member of the OHDSI community and is in the early stages of developing a Surgery and Perioperative Medicine Workgroup. He discusses that, as well as how he joined the community, how OHDSI impacted his COVID patient management in the last year, and more in this edition of the OHDSI Collaborator Spotlight.
EHDEN Launches Fourth, Largest, Open Call For Data Partners To Map To OMOP
 The EHDEN Consortium announced its fourth open call to all data custodians of electronic health records, claims, hospital and registry data across Europe to join in the goal of standardizing more than 100 million patient records to the OMOP common data model. EHDEN is currently working with 61 data partners following its first three open calls, and it has 26 small-to-medium enterprises (with more expected this year after a recent SME call) trained to work with the data partners in mapping the data to OMOP.
The EHDEN Consortium announced its fourth open call to all data custodians of electronic health records, claims, hospital and registry data across Europe to join in the goal of standardizing more than 100 million patient records to the OMOP common data model. EHDEN is currently working with 61 data partners following its first three open calls, and it has 26 small-to-medium enterprises (with more expected this year after a recent SME call) trained to work with the data partners in mapping the data to OMOP.
Data Partners can benefit from up to a maximum of €100,000 funding towards this mission, and this open call has an overall budget of €5 million. The current open call will run from April 15 to May 13. More information on EHDEN can be found here, and more details on this fourth open call for data partners on the EHDEN website.
The Quiet Driving Force for Observational Research, HADES Empowers a Global Community — Beyond Just OHDSI — To Generate Real-World Evidence
Network Study Updates, Including Pair Of Vaccine-Related Efforts, Presented To Community
 Six OHDSI network studies were presented during an April call to both inform the community about either ongoing or recently completed global research efforts, as well as calling for collaborators to join in these studies.
Six OHDSI network studies were presented during an April call to both inform the community about either ongoing or recently completed global research efforts, as well as calling for collaborators to join in these studies.
These 6-minute breakdowns were recorded and posted to the OHDSI YouTube channel, and all presentations are available below.
Cancer Risk Between H2 Blockers (Seng Chan You)
MSKAI- Musculoskeletal adverse events following hormonal treatment for breast cancer: Cohort Diagnostics to establish feasibility (Jenny Lane)
Covid-19 pandEmic impacts on mental health Related conditions Via multi-database nEtwork: a LongitutinaL Observational (CERVELLO) study (Carmen Olga-Torre)
Alpha-1 blocker for Palliating Inflammatory injury Severity (APIS) study (Aki Nishimura)
Calculating the background rates of adverse events of special interest (AESI) for the COVID vaccines (Xintong Li)
EUMAEUS – Evaluating Use of Methods for Adverse Event Under Surveillance (Martijn Schuemie)
Vaccine Surveillance Efforts Highlighted In Recent OHDSI Community Call
Collaborator Spotlight: Seng Chan You
 Seng Chan You is a medical doctor who majored in internal medicine from Severance Hospital in Seoul, South Korea. He received his Master of Medical Science at the same university, and then he earned his PhD in the Department of Biomedical Informatics at Ajou University, and he has been a leader in the OHDSI community over the last several years. Honored with the 2018 OHDSI Titan Award for Clinical Application, Chan has led the expansion of the OHDSI network into the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, including hosting the 2019 OHDSI Korea Symposium and assisting in the development of the 2020 OHDSI APAC Symposium.
Seng Chan You is a medical doctor who majored in internal medicine from Severance Hospital in Seoul, South Korea. He received his Master of Medical Science at the same university, and then he earned his PhD in the Department of Biomedical Informatics at Ajou University, and he has been a leader in the OHDSI community over the last several years. Honored with the 2018 OHDSI Titan Award for Clinical Application, Chan has led the expansion of the OHDSI network into the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, including hosting the 2019 OHDSI Korea Symposium and assisting in the development of the 2020 OHDSI APAC Symposium.
Chan, a leader in several OHDSI workgroups, recently led the effort to have South Korean HIRA data available to the OHDSI global community during the COVID-19 study-a-thon. He c0-led the study “Association of Ticagrelor vs Clopidogrel With Net Adverse Clinical Events in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention” which was published in JAMA in October 2020, and has co-authored many OHDSI network studies, including the LEGEND Hypertension study published in The Lancet.
Chan recently accepted a new position as a Research Assistant Professor at his alma mater. He recently shared thoughts on this new role, OHDSI’s growth in the Asia-Pacific region, leading the COVID-19 data sharing efforts, and plenty more in the latest edition of the OHDSI Collaborator Spotlight.
HL7 International and OHDSI Announce Collaboration to Provide Single Common Data Model for Sharing Information in Clinical Care and Observational Research
 Health Level Seven International (HL7®) and the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) network today announced a collaboration to address the sharing and tracking of data in the healthcare and research industries by creating a single common data model. The organizations will integrate HL7 Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR®) and OHDSI’s Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership (OMOP) common data model to achieve this goal.
Health Level Seven International (HL7®) and the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) network today announced a collaboration to address the sharing and tracking of data in the healthcare and research industries by creating a single common data model. The organizations will integrate HL7 Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR®) and OHDSI’s Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership (OMOP) common data model to achieve this goal.
The organizations will align their standards to capture data in a clearly defined way into a single common data model. This will allow clinicians as well as researchers to pull data from multiple sources and compile it in the same structure without degradation of the information. This endeavor has global implications with the potential to permit the clinical community to define the elements they need, package and share them in a consistent single structure.
“We are excited to have the OHDSI community join this partnership with HL7 to evolve community standards around observational research and clinical care,” said George Hripcsak, MD, MS, OHDSI’s coordinating center director. “These standards set the foundation for our mission of global, open-science research, and this partnership will accelerate the development of effective and safe treatments for diseases facing today’s global population.
HL7 International CEO Dr. Charles Jaffe, M.D., Ph.D., underscored the significance of this partnership. “The Covid-19 pandemic has emphasized the need to share global health and research data.” He continued, “Collaboration with OHDSI is critical to solving this challenge and will help our mutual vision of a world in which everyone can securely access and use the right data when and where they need it.”
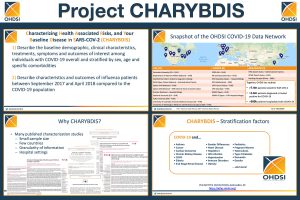
CHARYBDIS 2.0, Early SCYLLA Findings, Vaccine AESI Study Framework Discussed In OHDSI COVID-19 Research Presentation
 OHDSI research on COVID-19, which began with a memorable global study-a-thon last March, continues to progress in various ways throughout the world. Leaders in three of the largest network studies on the disease joined the Feb. 23 OHDSI community call to provide updates on these projects.
OHDSI research on COVID-19, which began with a memorable global study-a-thon last March, continues to progress in various ways throughout the world. Leaders in three of the largest network studies on the disease joined the Feb. 23 OHDSI community call to provide updates on these projects.
Kristin Kostka (IQVIA), Dani Prieto-Alhambra (University of Oxford) and George Hripcsak (Columbia University) gave presentations on ongoing work in both Project CHARYBDIS and SCYLLA, as well as OHDSI’s work with the FDA on the safety and effectiveness surveillance of the COVID-19 vaccines.
Videos and slides from each of the presentations are available here or on the Community Calls page.
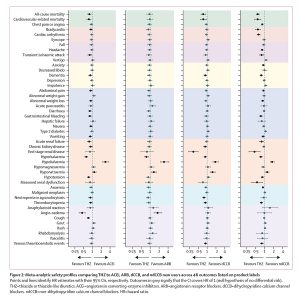
World’s Largest Study on ACE Inhibitors, ARBs Shows No Increased Patient Risk of COVID-19 Diagnosis, Complications
EHDEN Network Expands to 62 Data Partners Across 16 Nations Following Latest Open Call
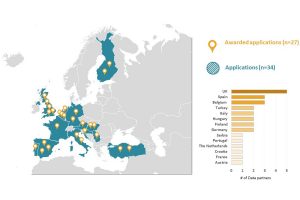 A critical aspect of the EHDEN project is for it to collaborate with data partners, such as hospitals, primary care providers, networks of both, regional datasets, claims databases and cohorts, with a view to harmonizing their clinical data locally to a common data model. Key to the success of the collaboration is the support of federated research via standardized analytical tools.
A critical aspect of the EHDEN project is for it to collaborate with data partners, such as hospitals, primary care providers, networks of both, regional datasets, claims databases and cohorts, with a view to harmonizing their clinical data locally to a common data model. Key to the success of the collaboration is the support of federated research via standardized analytical tools.
EHDEN, within the Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI), is a public-private partnership responding to the need to improve our speed to answers in real-world research. To this end, it has been creating a federated network, in collaboration with Data Partners, Small-to-Medium Size Enterprises (SMEs), the OHDSI framework and network, researchers, regulatory authorities and many others.
The EHDEN project is very pleased to announce the following 27 new Data Partners have been selected in our third open call for data partners. Collectively, our Data Partner Network now has 62 Data Partners, covering sixteen countries and have greater than 200 million anonymized patient health records that are being mapped to the common data model.
OHDSI Awarded $10 Million FDA Contract to Support Safety/Effectiveness Surveillance of Vaccines, Other Biological Products
 Researchers within the Observational Health Data Services and Informatics (OHDSI) community were recently awarded a $10 million contract from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to provide support to the Biologics Effectiveness and Safety (BEST) program, which was launched by the FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) in 2017.
Researchers within the Observational Health Data Services and Informatics (OHDSI) community were recently awarded a $10 million contract from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to provide support to the Biologics Effectiveness and Safety (BEST) program, which was launched by the FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) in 2017.
The lead research team, primarily comprised of OHDSI personnel from Columbia University, UCLA, and Northeastern University, will provide support to the BEST system in its mission to conduct safety and effectiveness surveillance of biologic products (vaccines, blood and blood products, tissues and advanced therapeutics).
Specific means of FDA support through this grant will include serving in a convening role to 1) develop methods related to using observational data from electronic health records and administrative claims to study the effectiveness and safety of biologics, 2) work collaboratively with FDA staff to plan, develop, coordinate, host and convene meetings and workshops, and 3) educate FDA staff and external stakeholders on the BEST infrastructure, capabilities, and applications that serve FDA and stakeholder needs.
Preferred ACS Treatment Not Associated With Better Patient Outcomes In Contemporary Clinical Practice According To Recent Multi-National Observational Study
 Ticagrelor, when compared with clopidogrel, was not associated with better outcomes for patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) treated with percutaneous coronary intervention in contemporary routine clinical practice according to a study published recently by the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) community.
Ticagrelor, when compared with clopidogrel, was not associated with better outcomes for patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) treated with percutaneous coronary intervention in contemporary routine clinical practice according to a study published recently by the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) community.
These findings raise doubts about current clinical guidelines for ACS treatment, which recommend ticagrelor over clopidogrel based on the findings of a single large sponsor-initiated clinical trial, PLATO, which was published in 2009.
This global network study, which included more than 60,000 patients with acute coronary syndrome who underwent PCI from two United States electronic health record-based databases and one nationwide South Korean database, is intended to provide greater detail about the characteristics of patients suffering from the disease, and also to help inform decision-making around the care of patients with ACS.
The study “Association of Ticagrelor vs Clopidogrel With Net Adverse Clinical Events in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention” was published Oct. 27, 2020 by JAMA.
OHDSI2020 Global Symposium Highlights Cutting-Edge Research, Community Advances; All Presentations, Collaborator Showcase Research Is Now Available
The 2020 OHDSI Global Symposium brought together a global research community for 18 hours of open science, international collaboration and community fun on Oct. 19. The day included presentations from community members, panels that brought together leaders from a variety of major healthcare organizations, as well as network sessions, the annual collaborator showcase, and plenty more.
Please check out this page for complete updates from the day, and follow the OHDSI Twitter and LinkedIn feeds for the #OHDSISocialShowcase, which will highlight all presentations from the 2020 Collaborator Showcase.
Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Shown To Be Younger, Healthier Than Influenza Patients Per Recent Global Observational Health Study
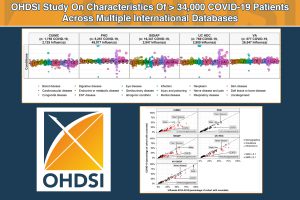 Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 were more likely male, younger, and, in both the US and Spain, had fewer comorbidities and lower medication use than hospitalized influenza patients according to a recent study published by the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) community.
Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 were more likely male, younger, and, in both the US and Spain, had fewer comorbidities and lower medication use than hospitalized influenza patients according to a recent study published by the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) community.
This global network study, which included more than 34,000 COVID-19 patients from across three continents, is intended to provide greater detail about the characteristics of patients suffering from the disease, and also to help inform decision-making around the care of hospitalized patients.
The study “Deep phenotyping of 34,128 adult patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in an international network study” was published Oct. 6 by Nature Communications and is available here.
Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 were more typically male in the US and Spain, but more often female in South Korea. The ages of patients varied, but in Spain and the US, the most common age groups were between 60 to 75. Patients hospitalized with influenza were typically older than those hospitalized with COVID-19, and more likely to be female.
OHDSI Symposium Panel – Building Trust: Evidence and its Communication
 Leaders from around the healthcare community will share their insights during a panel discussion entitled “Building Trust: Evidence and its Communication” during a highlight event of the 2020 OHDSI Global Symposium, which will be held Oct. 19, 2020. The panel will be held at 1 pm ET during the symposium, which is free for all attendees.
Leaders from around the healthcare community will share their insights during a panel discussion entitled “Building Trust: Evidence and its Communication” during a highlight event of the 2020 OHDSI Global Symposium, which will be held Oct. 19, 2020. The panel will be held at 1 pm ET during the symposium, which is free for all attendees.
This panel is scheduled to include:
• Amy Abernethy, MD, PhD, the Principal Deputy Commissioner of the U.S. FDA
• Patti Brennan, RN, PhD, the Director of the National Library of Medicine, NIH
• Magdalena Skipper, PhD, Editor in Chief, Nature
• Deborah Nelson, JD, Associate Professor of Investigative Journalism, University of Maryland
• Roni Caryn Rabin, MS, science reporter for the New York Times
George Hripcsak, MD, MS, Professor of Biomedical Informatics at Columbia University, will serve as moderator for this panel, which will take place at 1 pm ET during the main symposium
OHDSI Announces 18-Hour Global Symposium Schedule
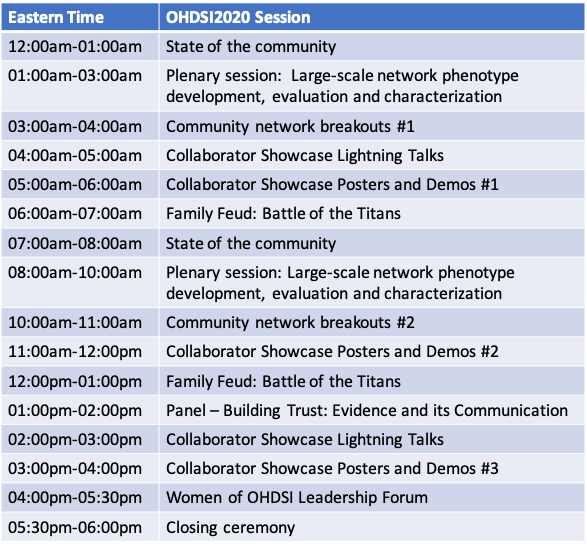 The OHDSI community will welcome both network veterans and newcomers from all parts of the world to join in an 18-hour celebration of open science, international collaboration, and community fun on Monday, Oct. 19 during the 2020 OHDSI Global Symposium.
The OHDSI community will welcome both network veterans and newcomers from all parts of the world to join in an 18-hour celebration of open science, international collaboration, and community fun on Monday, Oct. 19 during the 2020 OHDSI Global Symposium.
Part of a four-day event that will include both a day of tutorials on Oct. 18 and a two-day study-a-thon on Oct. 20-21, the global symposium will include many of the events that OHDSI veterans look forward to each year at the annual symposium … and a few surprises as well.
The symposium will be held virtually over Microsoft Teams, and registration is available here. Once again, there is no charge to attending the OHDSI Symposium.
Starting at midnight ET, our international community will have the opportunity to experience the full excitement of our 2020 symposium. Our Asia-Pacific collaborators will start in the afternoon, while the early risers in Europe can get a jump on their day with the state of the community address. As the symposium continues through the day, our European friends can enjoy panel discussions, poster sessions and a game show in the evening as our North American collaborators are in the middle of their symposium journey!
Collaborator Spotlight: Mui Van Zandt
Mui Van Zandt is a Director of Product Development at IQVIA, and she manages the OMOP Factory. Mui’s areas of expertise include software development, data conversions, agile process, and project management. Mui has gained extensive knowledge working on large patient databases in the OMOP model and the standard vocabularies that are needed to support these conversions.
Mui is an active contributor to the community through various OHDSI working groups. She is one of the co-leaders of the China OMOP CDM/Vocabulary working group. She leads two of the sub-working groups within the THEMIS working group. She has and continues to perform OMOP tutorial training to many different organizations and conferences, such as the OHDSI Symposiums, the China Hackathons, and individual universities.
A veteran of the OHDSI community, Mui recently shared some thoughts on her journey with the community, her work on the CDM and vocabularies, OHDSI progress, and more during the latest edition of the Collaborator Spotlight.
Podcast: Jenny Lane on the OHDSI Hydroxychloroquine Study
 Jenny Lane, co-lead author of the recently published “Risk of hydroxychloroquine alone and in combination with azithromycin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a multinational, retrospective study,” discussed the study and the 2020 journey of hydroxychloroquine during the debut episode of the OHDSI podcast, which is available below, as well as on Apple Podcasts, Podbean and other podcast apps.
Jenny Lane, co-lead author of the recently published “Risk of hydroxychloroquine alone and in combination with azithromycin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a multinational, retrospective study,” discussed the study and the 2020 journey of hydroxychloroquine during the debut episode of the OHDSI podcast, which is available below, as well as on Apple Podcasts, Podbean and other podcast apps.
Lane opens with a discussion on everything that went into the study, which was generated during the OHDSI COVID-19 study-a-thon in March, but she also talks about her own personal connection to hydroxychloroquine and its connection with rheumatoid arthritis, as well as the early clinical and methodological impact of the study during its preprint stage. She also discusses how open science and collaboration impacted this global study, and she provided insight on a recent OHDSI preprint she led, a study on the risk of depression, suicide and other psychological impacts in hydroxychloroquine treatment.
You can read more about the study here.
You can listen to the podcast below. Following a brief introduction, Jenny Lane joins the podcast at the 1:55 mark.
OHDSI Collaborators Publish 10 Principles Of LEGEND Project
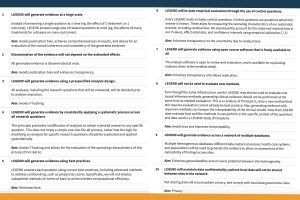 Evidence derived from existing health-care data, such as administrative claims and electronic health records, can fill evidence gaps in medicine. However, many claim such data cannot be used to estimate causal treatment effects because of the potential for observational study bias; for example, due to residual confounding. Other concerns include P hacking and publication bias.
Evidence derived from existing health-care data, such as administrative claims and electronic health records, can fill evidence gaps in medicine. However, many claim such data cannot be used to estimate causal treatment effects because of the potential for observational study bias; for example, due to residual confounding. Other concerns include P hacking and publication bias.
In response, an international group of OHDSI collaborators launched the Large-scale Evidence Generation and Evaluation across a Network of Databases (LEGEND) research initiative. Its mission is to generate evidence on the effects of medical interventions using observational health-care databases while addressing the aforementioned concerns by following a recently proposed paradigm. We define 10 principles of LEGEND that enshrine this new paradigm, prescribing the generation and dissemination of evidence on many research questions at once; for example, comparing all treatments for a disease for many outcomes, thus preventing publication bias. These questions are answered using a prespecified and systematic approach, avoiding P hacking. Best-practice statistical methods address measured confounding, and control questions (research questions where the answer is known) quantify potential residual bias. Finally, the evidence is generated in a network of databases to assess consistency by sharing open-source analytics code to enhance transparency and reproducibility, but without sharing patient-level information.
Here we detail the LEGEND principles and provide a generic overview of a LEGEND study. Our companion paper highlights an example study on the effects of hypertension treatments, and evaluates the internal and external validity of the evidence we generate.
Largest Global Study on Hydroxychloroquine Safety Finds Increased Cardiovascular Risk with Azithromycin
The combination of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) and azithromycin (AZM) has been linked to significant cardiovascular risks, including mortality, in the largest safety study ever performed on both HCQ and HCQ+AZM. This network study, led by the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics community, was recently published in Lancet Rheumatology.
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, HCQ treatment in the short term (30 days) was found to not carry an excess risk of complications associated with its use, but HCQ treatment in the long term had a 65% relative increase in cardiovascular-related mortality, compared to sulfasalazine.
HCQ + AZM had a cardiovascular mortality risk that was more than twice (2.19) as high as the comparative treatment even in the short term based on findings from more than 320,000 users of that combination therapy. This treatment also produced a 15-20% increased rate of angina/chest pain and heart failure.
The full paper is available here.
OHDSI Obtains Grant Towards Global Research On COVID-19 Treatments
 An international cohort of OHDSI collaborators obtained a grant from the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator to lead an effort to compare the effectiveness of treatments, including corticosteroids such as dexamethasone, under current evaluation for COVID-19 across an international observational data network. The Therapeutics Accelerator is an initiative launched by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and Mastercard to speed up the response to the COVID-19 pandemic by identifying, assessing, developing, and scaling up treatments.
An international cohort of OHDSI collaborators obtained a grant from the COVID-19 Therapeutics Accelerator to lead an effort to compare the effectiveness of treatments, including corticosteroids such as dexamethasone, under current evaluation for COVID-19 across an international observational data network. The Therapeutics Accelerator is an initiative launched by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, Wellcome, and Mastercard to speed up the response to the COVID-19 pandemic by identifying, assessing, developing, and scaling up treatments.
Researchers from the University of Oxford, Columbia University, UCLA and Erasmus University Medical Center are leading this work through Project SCYLLA (SARS-Cov-2 Large-scale Longitudinal Analyses), one of the emerging efforts to come from OHDSI’s global work surrounding COVID-19 research.
“We are so appreciative that the donors of the Therapeutics Accelerator support our work around studying the effectiveness and safety of potential COVID-19 medicines,” says Daniel Prieto-Alhambra, Professor of Pharmaco- and Device Epidemiology at Oxford and co-PI on the project. “Their funding will help us learn which treatments are showing potential throughout an international cohort of patients. Every ounce of knowledge is a building block that will eventually lead us out of this global crisis.”
Collaborator Spotlight: Anthony Sena
 Anthony Sena is an Associate Director of Epidemiology Analytics at Janssen Research and Development where he architects software solutions and data platforms for the analysis and application of observational data sources. Anthony’s areas of expertise include web application development, data modeling, information visualization, technology infrastructure, project management, and informatics. A collaborator on a number of open-source software solutions in OHDSI and one of the co-leads of the ATLAS & WebAPI working group, he has taken a prominent role in the recent CHARYBDIS Project, a characterization study to understand the disease natural history of COVID-19. His focus is on expanding the capabilities of the OHDSI open-source solution architecture to enable transparent and reproducible research using observational data.
Anthony Sena is an Associate Director of Epidemiology Analytics at Janssen Research and Development where he architects software solutions and data platforms for the analysis and application of observational data sources. Anthony’s areas of expertise include web application development, data modeling, information visualization, technology infrastructure, project management, and informatics. A collaborator on a number of open-source software solutions in OHDSI and one of the co-leads of the ATLAS & WebAPI working group, he has taken a prominent role in the recent CHARYBDIS Project, a characterization study to understand the disease natural history of COVID-19. His focus is on expanding the capabilities of the OHDSI open-source solution architecture to enable transparent and reproducible research using observational data.
Prior to joining Janssen Research and Development, Anthony held many leadership and technical roles of increasing responsibility across a range of business sectors including energy, pharmaceuticals, retail and financial services. He recently discussed his journey to OHDSI, his work with open-source tools, and some of his most important projects, during the latest Collaborator Spotlight.
EMA Announces Partnership With EHDEN To Monitor COVID-19 Treatments
 The European Medicines Agency recently announced an infrastructure to support the monitoring of the efficacy and safety of COVID-19 treatments and vaccines when used in day-to-day clinical practice. The EMA will work with EHDEN on this initiative to establish a European framework and research network for the conduct of multicenter cohort studies on the use of medicines in COVID-19 patients.
The European Medicines Agency recently announced an infrastructure to support the monitoring of the efficacy and safety of COVID-19 treatments and vaccines when used in day-to-day clinical practice. The EMA will work with EHDEN on this initiative to establish a European framework and research network for the conduct of multicenter cohort studies on the use of medicines in COVID-19 patients.
This will be a one-year EMA-funded project, which includes data sources from eight European countries standardized to the OMOP-Common Data Model, and is contracted to IQVIA as the coordinating partner. OHDSI and EHDEN leaders from both the Erasmus Medical Center and the University of Oxford will help drive this important work.
“This is precisely what EHDEN was set up for,” says Peter Rijnbeek, associate professor at Erasmus. “We are creating an international, open science network in Europe, based on a common data model, standardized analytics, tools, and methodologies. It’s exciting to participate in this project and further strengthen our collaboration with the EMA.”
EMA References OHDSI Efforts In Latest Revision Of Scientific Best Practices In Observational Research
 The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provided guidance for scientific best practices in observational research in the recently released 8th revision of its guidelines. This work aligns with OHDSI’s mission, and our global community was proud to see multiple OHDSI efforts, including a pair of COVID-19 studies, have informed and supported their recommendations.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) provided guidance for scientific best practices in observational research in the recently released 8th revision of its guidelines. This work aligns with OHDSI’s mission, and our global community was proud to see multiple OHDSI efforts, including a pair of COVID-19 studies, have informed and supported their recommendations.
The foreword in “The European Network of Centres for Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacovigilance (ENCePP) Guide on Methodological Standards in Pharmacoepidemiology” highlighted a pair of community preprints currently undergoing peer review.
2020 EU Symposium Collaborators Share Research As Part Of Virtual Showcase
 Though the 2020 European Symposium was canceled and replaced with the COVID-19 Study-A-Thon, many community members still shared their research that had been accepted for the Collaborators Showcase. Those posters, along with abstracts and other links, were highlighted over the OHDSI social platforms, and are all available here.
Though the 2020 European Symposium was canceled and replaced with the COVID-19 Study-A-Thon, many community members still shared their research that had been accepted for the Collaborators Showcase. Those posters, along with abstracts and other links, were highlighted over the OHDSI social platforms, and are all available here.
This research comes from around the world and highlights the breadth and variety of OHDSI research in a pre-COVID world.
No Clear Risk For COVID-19 Diagnosis or Hospitalization From ACE/ARB Use According To Recent OHDSI Preprint
 The Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) collaboration released a preprint entitled “Renin-angiotensin system blockers and susceptibility to COVID-19: a multinational open science cohort study.”
The Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) collaboration released a preprint entitled “Renin-angiotensin system blockers and susceptibility to COVID-19: a multinational open science cohort study.”
Preprints are preliminary reports of work that have not been certified by peer review. They should not be relied on to guide clinical practice or health-related behavior and should not be reported in news media as established information.
The preprint is available here.
There was no clear increased risk of COVID-19 diagnosis, hospitalization, or subsequent complications found for users of either angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEs) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) among a multinational cohort of more than 1.1 million patients using antihypertensives.
This study, the most comprehensive one to date of COVID-19 susceptibility risks for antihypertensive users, examined electronic health records from a trio of data sources from the United States and Spain (Columbia University Irving Medical Center, the Department of Veteran Affairs and SIDIAP) to conduct a systematic cohort study of ACE, ARB, calcium channel blocker (CCB) and thiazide diuretic (THZ) users.
“We currently lack reliable, transparent and generalizable evidence to inform antihypertensive choice in light of COVID-19,” says Dr. Marc Suchard, a professor at UCLA and research team leader. “This work strives to openly and reproducibly leverage real-world data to help.”
As a consequence, the study, powered by open-source tools and global collaboration within the OHDSI community, reinforces current clinical guidelines surrounding antihypertensive therapy. The findings indicate that patients should continue their ACE or ARB therapy, despite early concerns about potential risks.
Furthermore, the findings showed no clinical reason to switch from an ARB to ACE to minimize COVID-19 risk. “Based on our results, if there is a risk difference, it’s marginal and would be very challenging to further refine outside such a large-scale international study,” Dr. Suchard says.
The International COVID-ACE Receptor Inhibition Utilization and Safety (ICARIUS) protocol, code, and results are all available for further exploration at https://github.com/ohdsi-studies/Covid19Icarius.
Collaborator Spotlight: Kees van Bochove
 Kees van Bochove is the founder and CEO of The Hyve, a 40-person international company dedicated to the support and facilitation of open source, open standards, and open data in biomedical research. He studied Computer Science at the University of Utrecht and Bioinformatics at VU University Amsterdam and Tufts University in Boston. Kees is active in many open-source software development communities such as i2b2/tranSMART, cBioPortal, OHDSI, RADAR, Galaxy, etc. Through his many years of experience in open source software and standards development in biomedical informatics, Kees has gained a deep understanding of all aspects of collaborative open source development and open data science, including open source community building and governance, software quality, and sustainability requirements, data workflows, etc.
Kees van Bochove is the founder and CEO of The Hyve, a 40-person international company dedicated to the support and facilitation of open source, open standards, and open data in biomedical research. He studied Computer Science at the University of Utrecht and Bioinformatics at VU University Amsterdam and Tufts University in Boston. Kees is active in many open-source software development communities such as i2b2/tranSMART, cBioPortal, OHDSI, RADAR, Galaxy, etc. Through his many years of experience in open source software and standards development in biomedical informatics, Kees has gained a deep understanding of all aspects of collaborative open source development and open data science, including open source community building and governance, software quality, and sustainability requirements, data workflows, etc.
Kees has been involved in OHDSI initially via the IMI EMIF project starting in 2013 and has been building a team around OMOP/OHDSI through the EMIF collaboration, working with a.o. Janssen and ErasmusMC as well as by providing OMOP mapping and OHDSI installation and support services to several pharmaceutical companies. Kees was also involved in planning the first OHDSI Europe meeting in March 2018, and he hosted a subsequent follow-up workshop to introduce OHDSI to a number of European national health-data initiatives (from a.o. The Netherlands, Germany, Switzerland, and Denmark) in May 2018. The Hyve is also leading WP4 in the IMI EHDEN project, which is one of the largest components of this important project, laying the technical groundwork and building data conversion and quality management tools for further developing the European and global OHDSI community.
(Click the link in the headline for a Q&A with Kees)
OHDSI Presents Study-A-Thon Findings At 2020 EULAR E-Congress
 OHDSI collaborators shared important findings generated from the 2020 Barcelona Study-A-Thon at the recent 2020 EULAR E-Congress, held June 3-6, 2020.
OHDSI collaborators shared important findings generated from the 2020 Barcelona Study-A-Thon at the recent 2020 EULAR E-Congress, held June 3-6, 2020.
“It was an honor for our team to share our findings at the 2020 EULAR Congress,” said Daniel Prieto-Alhambra, who led the Barcelona Study-A-Thon, and who also served on the EULAR Congress Programme Committee. “The experience in Barcelona was an enjoyable event, but the real-world studies and findings generated from that week can have a powerful impact on the field of rheumatology, and we couldn’t be prouder of that.”
Posters, slides and Cynthia Yang’s oral presentation can all be found by clicking here.
Seek COVER, First COVID-19 Prediction Study Generated During OHDSI Study-A-Thon, Released in OHDSI Preprint
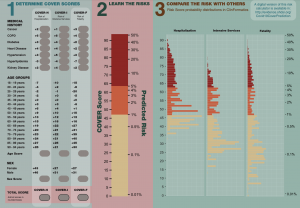 The first Patient-Level Prediction paper has been sent to MedRxiv and is being submitted for peer review. This study “Seek COVER: Development and validation of a personalized risk calculator for COVID-19 outcomes in an international network” is designed to inform individual behavioral choices and help design shielding strategies during de-confinement.
The first Patient-Level Prediction paper has been sent to MedRxiv and is being submitted for peer review. This study “Seek COVER: Development and validation of a personalized risk calculator for COVID-19 outcomes in an international network” is designed to inform individual behavioral choices and help design shielding strategies during de-confinement.
Led by co-first authors Ross Williams and Aniek Markus, the team designed a nine-predictor COVID-19 Estimated Risk (COVER) model that was validated using more than 43,000 COVID patients (following initial development and validation using more than 6.8 million patients with influenza or flu-like symptoms). This model predicts hospitalization, intensive services, and death, and can help provide reassurance for low-risk patients, while shielding high-risk patients, as many start to enter the de-confinement stage of the pandemic.
Peter Rijnbeek is the corresponding author, and both he and Jenna Reps are co-last authors. Overall there are 43 authors involved in the study, once again highlighting the global collaborative nature of the OHDSI community. Congratulations to all who were involved in this work.
Collaborator Spotlight: Kristin Kostka
 Kristin Kostka is an Associate Director at IQVIA running the OMOP Data Network and a perennial collaborator in the OHDSI community. In her work, Kristin partners with hospitals, payers and healthcare providers to help organizations unlock the power of institutional data and connect with the world’s largest observational health data network.
Kristin Kostka is an Associate Director at IQVIA running the OMOP Data Network and a perennial collaborator in the OHDSI community. In her work, Kristin partners with hospitals, payers and healthcare providers to help organizations unlock the power of institutional data and connect with the world’s largest observational health data network.
Kristin has over 10 years of experience leading real-world evidence generation studies, designing and implementing enterprise patient data lakes, conducting large-scale multinational clinical trials and preparing regularly submissions. Within OHDSI, Kristin sits on the OHDSI Steering Committee, the US Symposium Scientific Committee, the Women of OHDSI group, the OHDSI Study Nurture Committee and regularly leads OHDSI network studies. Kristin co-authored three chapters of the Book of OHDSI (Where to Begin, Defining Cohorts and OHDSI Network Research). Her OHDSI passion project is the idea of “studies on studies” — evaluating the best way to disseminate evidence once its generated. Kristin currently serves as a member of the OHDSI COVID-19 Study-a-thon Core Team facilitating follow-on work from the recent virtual study-a-thon. She is also a Co-Principal Investigator on Project CHARYBDIS (Characterizing Health Associated Risks, and Your Baseline Disease In SARS-COV-2).
Kristin is a recipient of many industry awards, including the 2020 Elon University Young Alumni Council “Top 10 Under 10” Alumni Award, a 2018 OHDSI Titan Award for Community Collaboration, a 3-time recipient of Deloitte Outstanding Performance Award and an 8-time recipient of the Deloitte Applause Award for exceptional client service. She holds a Bachelor’s degree in Exercise Science from Elon University and a Master’s in Public Health in Epidemiology from Boston University School of Public Health.
(Click the link in the headline for a Q&A with Kristin)
Multi-Institutional Characterization Study on Hospitalized COVID Patients, And Comparison To Hospitalized Influenza Patients, Released in OHDSI Preprint
 The Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) collaboration released a preprint on an international characterization of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and a comparison with those previously hospitalized with influenza.
The Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) collaboration released a preprint on an international characterization of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and a comparison with those previously hospitalized with influenza.
Preprints are preliminary reports of work that have not been certified by peer review. They should not be relied on to guide clinical practice or health-related behavior and should not be reported in news media as established information.
The preprint is available here.
The characteristics (demographics, prior conditions and medication use) of more than 6,800 COVID-positive patients from four databases (Columbia, Stanford, the Department of Veterans Affairs and the South Korean Health Insurance Review & Assessment) were reported in this study and were compared to more than 52,000 patients hospitalized with influenza between 2014-19.
Compared to 52,422 individuals hospitalized with influenza, patients admitted with COVID-19 were more likely male, younger, and, in the US, had fewer comorbidities and lower medication use.
EHDEN Academy Goes Live as Free Resource in Real-World Health Research
 The European Health Data & Evidence Network (EHDEN) today announced the launch of the EHDEN Academy in Europe as an online educational resource for anyone working in the domain of real-world data use, and real-world evidence generation, with the aim of becoming a primary resource.
The European Health Data & Evidence Network (EHDEN) today announced the launch of the EHDEN Academy in Europe as an online educational resource for anyone working in the domain of real-world data use, and real-world evidence generation, with the aim of becoming a primary resource.An IMI2 (Innovative Medicines Initiative) EHDEN project, the EHDEN Academy’s goal is to build upon the foundations of the EHDEN project and its collaboration with the OHDSI community. The EHDEN Academy aims to be a resource for all those who generate and utilize data, work technically with it (e.g. ETL and mapping of data to the OMOP common data model), and are involved in the methodological development and use of standardized analytical tools within the OHDSI framework.
As the current SARS-CoV-2 pandemic is showing us, the ability to collaborate and work with real-world data is critical to clinical decision-making, planning, and management decisions. As such, EHDEN is responding to the pandemic via its involvement in the OHDSI COVID-19 Virtual Study-a-thon, a COVID-19 Data Partner call, also supporting education in using real-world evidence at this critical time via the EHDEN Academy.
88 Hours: OHDSI’s Signature Moment
 The time was meant for highlighting OHDSI capabilities, not testing them. The hours were meant to sharing global research, not sharing in global research.
The time was meant for highlighting OHDSI capabilities, not testing them. The hours were meant to sharing global research, not sharing in global research.
The Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) community held a COVID-19 global, virtual study-a-thon March 26-29, believing that a network of people who valued both collaboration and open science could make a meaningful impact on the current global pandemic.
How? Nobody was quite sure in the moment, but they were confident they would figure it out.
“We chose an ambitious path and relied on our community and infrastructure to lead the way,” said Patrick Ryan. “In simple terms, efforts within our community over the past 88 months set the foundation for OHDSI’s most important and impactful 88 hours.”
(Click here for the full feature story on the OHDSI COVID-19 study-a-thon)
Largest Observational Study on Hydroxychloroquine Safety Profile Released in OHDSI Preprint
 The Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) collaboration released a preprint on preliminary findings from the largest study ever completed on the safety profile of hydroxychloroquine, a drug currently being evaluated as a potential treatment for COVID-19.
The Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) collaboration released a preprint on preliminary findings from the largest study ever completed on the safety profile of hydroxychloroquine, a drug currently being evaluated as a potential treatment for COVID-19.
Preprints are preliminary reports of work that have not been certified by peer review. They should not be relied on to guide clinical practice or health-related behavior and should not be reported in news media as established information.
The preprint is available here.
The combined short-term use of hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin resulted in nearly 60% higher rate of cardiovascular-related mortality (calHR 2.19; (1.22-3.94)) than the combined use of hydroxychloroquine and amoxicillin. While not as high, there was also an advanced risk for both chest pain/angina (calHR 1.15 (1.05-1.26)) and heart failure (calHR 1.22 (1.02-1.45)) when azithromycin was added to hydroxychloroquine treatment.
These findings were generated from an international database of more than 950,000 users of hydroxychloroquine, including approximately 320,000 who used it in combination with azithromycin.
The short-term effect of hydroxychloroquine as a treatment drug was not found to have an excess risk by itself when compared to sulfasalazine among a large set of patients (950,769 and 306,706, respectively) being treated for rheumatoid arthritis.
Patients from five different countries (Germany, Japan, Spain, the United State, and the United Kingdom) were included in this study, the first to be shared via preprint from a four-day OHDSI COVID-19 study-a-thon, which brought together a global community to design and execute observational studies to generate real-world evidence and help inform the current global pandemic.
These are preliminary findings that are currently in the peer-review process. They should not be relied on to guide clinical practice or health-related behavior and should not be reported in news media as established information.
OHDSI Collaboration Designs COVID-19 Studies For International Observational Data Network
 A four-day global collaboration within the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) community designed and began executing studies on an international set of observational health databases (including insurance claims and electronic health records) to aid decision-making during the current COVID-19 pandemic.
A four-day global collaboration within the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) community designed and began executing studies on an international set of observational health databases (including insurance claims and electronic health records) to aid decision-making during the current COVID-19 pandemic.
One study is the first large-scale characterization of COVID-19 patients in both the United States and Asia; six databases with COVID-19 patients located in both the U.S. and South Korea already started running data on this project, and other databases are being sought to collaborate in this network study.
The largest study ever conducted on the safety of hydroxychloroquine was designed and executed across an international set of databases. This study of more than 130,000 patients from the USA, England, Germany and South Korea focuses on the overall safety profile of hydroxychloroquine, a drug currently being evaluated as a potential treatment for COVID-19.
The third study designed the first prediction model externally validated on COVID-19 patients to support triage decisions in an effort to ‘flatten the curve’. This model, which determines which patients presenting with symptoms are most likely to require hospitalization, was developed against US data and then tested on South Korean data.
More than 330 people from 30 nations registered to collaborate in this 88-hour virtual study-a-thon, which concluded March 29 with a global presentation from multiple study leads to announce both designs and preliminary findings. Results are currently being evaluated and papers are actively being submitted to journals for peer review.
OHDSI Kicks Off International Collaborative to Generate Real-World Evidence on COVID-19 with Virtual Study-a-thon March 26-29
 The Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) international community will host a COVID-19 virtual study-a-thon this week (March 26-29) to inform healthcare decision-making in response to the current global pandemic.
The Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) international community will host a COVID-19 virtual study-a-thon this week (March 26-29) to inform healthcare decision-making in response to the current global pandemic.
More than 290 people from 29 different countries have registered for the four-day online event, which will be led by researchers from Oxford University, Erasmus Medical Center, Columbia University, UCLA, Ajou University, Janssen Research and Development, and IQVIA, with active participation across government, industry, and academia.
Held in lieu of the canceled OHDSI European Symposium, this event is structured to have two main goals: (1) to generate immediate real-world evidence on prioritized questions shared by national governments, public health agencies, health-related institutions, and community members; and (2) to design COVID-19-specific studies that can be validated and available to run when such data is available.
Cervical Cancer Risk Decreases In Users Of Copper IUDs vs. Hormonal IUDs; Research Team Seeks Community Involvement For Network Study
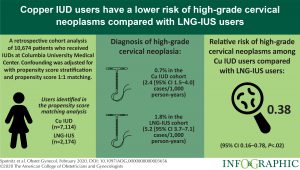 Patients who used copper intrauterine devices (Cu IUD) were found to have a lower risk of high-grade cervical neoplasms (cervical cancer) compared to users of the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (LNG-IUS), according to a Columbia study recently published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Patients who used copper intrauterine devices (Cu IUD) were found to have a lower risk of high-grade cervical neoplasms (cervical cancer) compared to users of the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (LNG-IUS), according to a Columbia study recently published in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Studies from the 1980s suggested a reduced risk of cervical cancer among women who used an intrauterine contraceptive, though those studies did not differentiate between the varying types of IUDs. Furthermore, much of the data from those studies was collected prior to the availability of most hormonal IUDs (LNG-IUS).
Spotnitz noted that the research team hopes to lead a network study across other databases within the OHDSI network, which spans 19 countries, 133 unique databases converted to the OMOP CDM, and more than one billion patient records. For more information on the study, check out this forum post, or email him directly at mes2165@cumc.columbia.edu.
OHDSI Korea Symposium Page Is Live, Includes Video Of All Sessions, Photo Recap
 The 2019 OHDSI Korea Symposium took place Dec. 12-14 at the Konjiam Resort in Gwangju and attracted 330 people to the main symposium on Dec. 13. It was another great gathering of OHDSI collaborators — both veterans and those just starting on the journey — to learn from each other, present their own research, and network together.
The 2019 OHDSI Korea Symposium took place Dec. 12-14 at the Konjiam Resort in Gwangju and attracted 330 people to the main symposium on Dec. 13. It was another great gathering of OHDSI collaborators — both veterans and those just starting on the journey — to learn from each other, present their own research, and network together.
This page includes a photo gallery from the event, as well as videos all five sessions from the main symposium, as well as tutorials. Sessions included an introduction to both OHDSI and EHDEN, multiple presentations on OHDSI Community in Action, and sharing the international experience from the Asian-Pacific Region.
Recommended Diuretic Causes More Side Effects than Similar Hypertension Drug, Per Recent LEGEND Study
Chlorthalidone, the guideline-recommended diuretic for lowering blood pressure, causes more serious side effects than hydrochlorothiazide, a similarly effective diuretic, according to a recent OHDSI study. The findings, published in JAMA Internal Medicine, contrast with current treatment guidelines recommending chlorthalidone over hydrochlorothiazide.
The researchers found that patients taking chlorthalidone had nearly three times the risk of developing dangerously low levels of potassium and a greater risk of other electrolyte imbalances and kidney problems compared with those taking hydrochlorothiazide. Information from the largest individual database studied by the team revealed that 6.3% of patients treated with chlorthalidone experienced hypokalemia (low blood potassium), compared with 1.9% of patients who were treated with hydrochlorothiazide.
“Doctors prescribing chlorthalidone should monitor for certain side effects in their patients,” says George Hripcsak, MD, MS, chair and Vivian Beaumont Allen Professor of Biomedical Informatics at Columbia University and lead author of the study.
Methods Benchmark Can Aid Trust In Observational Research, Per Recent OHDSI Study
 The prevalence of electronic healthcare data allows researchers the opportunity to study the effects of medical treatments. However, confidence in the results of such observational research is typically low, for example, because different studies on the same question often produce conflicting results, even when using the same data. We need to answer the question “to what extent can we trust observational research?”
The prevalence of electronic healthcare data allows researchers the opportunity to study the effects of medical treatments. However, confidence in the results of such observational research is typically low, for example, because different studies on the same question often produce conflicting results, even when using the same data. We need to answer the question “to what extent can we trust observational research?”
Led by Martijn Schuemie, OHDSI researchers recently published “How Confident Are We About Observational Findings in Healthcare: A Benchmark Study” in the Harvard Data Science Review to tackle this important issue. This paper presents the OHDSI Methods Benchmark to evaluate five methods commonly used in observational research (new-user cohort, self-controlled cohort, case-control, case-crossover, and self-controlled case series designs) over a network of four large databases standardized to the OMOP Common Data Model.
Using both negative and positive controls (questions where the answer is known), a set of metrics and open-source software tools developed within the OHDSI community, the research team determined that most commonly used approaches to effect-estimation observational studies are falling short of expected confidence levels. Selection bias, confounding, and misspecification are among the sources of systematic error that plagues the validity of potentially important findings within the healthcare community.
OHDSI Q&A: Dani Prieto-Alhambra Discusses RA Study-A-Thon, EU Symposium
 When Dani Prieto-Alhambra discussed the Oxford Study-A-Thon at the 2019 U.S. Symposium, he introduced his talk as the “conversion of himself and 30-35 colleagues to the OMOP Common Data Model and to the OHDSI way of doing things.”
When Dani Prieto-Alhambra discussed the Oxford Study-A-Thon at the 2019 U.S. Symposium, he introduced his talk as the “conversion of himself and 30-35 colleagues to the OMOP Common Data Model and to the OHDSI way of doing things.”
After sharing the incredible research that would eventually lead to a published study in The Lancet Rheumatology, he didn’t wait long to welcome new converts to the OHDSI community. Prieto-Alhambra coordinated the 2020 Barcelona Study-A-Thon on rheumatoid arthritis (RA); you can read the OHDSI release about the event here.
He recently discussed several aspects of the study-a-thon with OHDSI.org, and he also touched on the 2020 OHDSI European Symposium, which will be held March 27-29 at Oxford. Abstracts for the Symposium are due Friday, Feb. 14; more information on abstract submission and other areas of participation is available here.
EHDEN Launches Second Open Call For SMEs
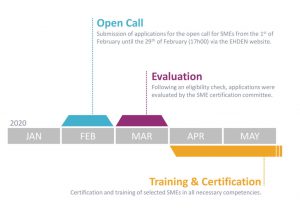 The OHDSI community has been a proud collaborator with the European Health Data & Evidence Network (EHDEN) since the EHDEN launch in 2018. An IMI 2 consortium, EHDEN looks standardize more than 100 million patient records across Europe from different geographic areas and different data sources over the coming five years. Mapping of healthcare data to the OMOP-CDM will facilitate the re-use for a variety of purposes, enhancing and accelerating research and healthcare decision-making for global benefit. To this end, EHDEN will create an SME eco-system in Europe that supports data sources and other stakeholders in mapping and using data.
The OHDSI community has been a proud collaborator with the European Health Data & Evidence Network (EHDEN) since the EHDEN launch in 2018. An IMI 2 consortium, EHDEN looks standardize more than 100 million patient records across Europe from different geographic areas and different data sources over the coming five years. Mapping of healthcare data to the OMOP-CDM will facilitate the re-use for a variety of purposes, enhancing and accelerating research and healthcare decision-making for global benefit. To this end, EHDEN will create an SME eco-system in Europe that supports data sources and other stakeholders in mapping and using data.
EHDEN recently announced that it has launched the second open call for SMEs to apply for training and certification to convert health data from various formats to the OMOP common data model. This second open call will run throughout the month of February, concluding on the 29th (17:00 CET).
If this prospect interests you, visit the EHDEN open call for SMEs page for more details and to submit your application. The EHDEN Consortium is looking forward to your potential application and to collaborate with you.
Invested Stakeholders, OHDSI Tools/Practices Drive Successful Rheumatoid Arthritis Study-A-Thon In Barcelona
 One year after a similar study-a-thon at Oxford resulted in a knee replacement study published by The Lancet Rheumatology, 40 stakeholders from across industry, academia, and health systems — representing 10 different nations and 14 observational databases — gathered to participate in a OHDSI-EHDEN Study-a-thon and run the world’s largest network studies on Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA).
One year after a similar study-a-thon at Oxford resulted in a knee replacement study published by The Lancet Rheumatology, 40 stakeholders from across industry, academia, and health systems — representing 10 different nations and 14 observational databases — gathered to participate in a OHDSI-EHDEN Study-a-thon and run the world’s largest network studies on Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA).
The Study-a-thon was held at the Barcelona Biomedical Research Park Jan. 13-17 and focused on three areas during the five-day gathering: (1) characterizing drug treatment patterns; (2) developing a population-level effect estimation, examining the comparative safety of first-line Disease Modifying Anti Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) for safety profiles and multiple adverse outcomes; and (3) creating a patient-level prediction analysis to determine high-risk RA patients for specific adverse outcomes. The OHDSI-EHDEN community conducted observational analyses across a secure, distributed network of electronic health records and insurance claims data, collectively representing more than 1.1 million patients with RA.
“It was an honor to collaborate with so many leaders in the battle against RA, and I truly believe we made a meaningful difference within one week,” said Patrick Ryan. “I am continually amazed at what can be accomplished when you combine invested stakeholders and high-level analytic tools in an open-science setting.”
EHDEN Academy Shows Early Success, Could Provide Educational Foundation For OHDSI Network In 2020
 As an associate professor at Erasmus Medical Center, Peter Rijnbeek appreciates the importance of a strong, effective educational program. He has been pleased with the early progress of the EHDEN Academy, a program that should provide a broad impact for the OHDSI community once it becomes publicly available in early 2020.
As an associate professor at Erasmus Medical Center, Peter Rijnbeek appreciates the importance of a strong, effective educational program. He has been pleased with the early progress of the EHDEN Academy, a program that should provide a broad impact for the OHDSI community once it becomes publicly available in early 2020.
The EHDEN Academy, an E-learning environment developed by the EHDEN (European Health Data & Evidence Network) Consortium, was initially developed to educate SMEs (Small and Medium Enterprises) about the tools and best practices used by both EHDEN and OHDSI. There are five training courses Rijnbeek and his EHDEN colleagues felt would provide a baseline of knowledge needed to certify a support network to map a growing set of European databases to the OMOP common data model.
Book Of OHDSI, Now Available In English/Korean Versions, Provides Central Knowledge Repository For Collaborators
 One memorable moment (during a day full of them) at the 2019 OHDSI U.S. Symposium came during Martijn Schuemie’s talk on best practices within the community. With a significant number of first-timers in the Bethesda North Marriott ballroom that day, Schuemie may have caused a moment of panic for some by noting all the different locations collaborators could search to follow the preferred OHDSI methods. The panic quickly turned to celebration.
One memorable moment (during a day full of them) at the 2019 OHDSI U.S. Symposium came during Martijn Schuemie’s talk on best practices within the community. With a significant number of first-timers in the Bethesda North Marriott ballroom that day, Schuemie may have caused a moment of panic for some by noting all the different locations collaborators could search to follow the preferred OHDSI methods. The panic quickly turned to celebration.
The unveiling of The Book of OHDSI at the 2019 U.S. Symposium was the culmination of months of community work, and it serves to provide the community with a central knowledge repository for all aspects of OHDSI. Twenty chapters within five sections (the OHDSI Community, Uniform Data Representation, Data Analytics, Evidence Quality, and OHDSI Studies) were written to empower any new researcher with the ability to generate real-world evidence to improve the healthcare community.
2019 Symposium Tutorials Available, Provide Education On Multiple Tools, Practices Within Community
 While OHDSI collaborators continue to seek new and innovative ways to train the growing community in the tools and best practices of the network, face-to-face tutorials remain an effective method for educating both newcomers and veterans. During the 2019 OHDSI U.S. Symposium, there were six tutorials held, and you can watch any or all of them now on the OHDSI YouTube channel.
While OHDSI collaborators continue to seek new and innovative ways to train the growing community in the tools and best practices of the network, face-to-face tutorials remain an effective method for educating both newcomers and veterans. During the 2019 OHDSI U.S. Symposium, there were six tutorials held, and you can watch any or all of them now on the OHDSI YouTube channel.
Use the headline link to get access to all six tutorials, including videos, materials, information and more.
First Korea Tutorial, OHDSI Japan Formation Highlight Exciting Asian Progress Before Korea Symposium
 The first official OHDSI Korea tutorial was held Oct. 23 in the Grand Ambassador Seoul, and it served as an important lead event for the upcoming OHDSI Korea Symposium, which takes place Dec. 12-14 at the Konjiam Resort in Gyeonggi-Do, Korea. The enthusiasm in the room was palpable, and the energy that has been building in Korea should lead to an exciting Symposium.
The first official OHDSI Korea tutorial was held Oct. 23 in the Grand Ambassador Seoul, and it served as an important lead event for the upcoming OHDSI Korea Symposium, which takes place Dec. 12-14 at the Konjiam Resort in Gyeonggi-Do, Korea. The enthusiasm in the room was palpable, and the energy that has been building in Korea should lead to an exciting Symposium.
While Korea first started working with OHDSI and the OMOP Common Data Model in 2014, workshops in the country had been limited to smaller Ajou University-sessions within hospitals. This was the first event that was formalized by OHDSI collaborators and open to all. There was a heavy morning focus on how to run a network study, which followed an OHDSI Introduction by Mui Van Zandt.
OHDSI Introduction At Georgia Tech Educates Both Students And Professor
 The first-ever OHDSI block of the CS6440 course at Georgia Tech, held over a six-week span this past fall, was both educational and inspiring, and it reinforced the strengths that have carried OHDSI from concept to major player in the real-world analytics ecosystem.
The first-ever OHDSI block of the CS6440 course at Georgia Tech, held over a six-week span this past fall, was both educational and inspiring, and it reinforced the strengths that have carried OHDSI from concept to major player in the real-world analytics ecosystem.
The professor felt it from the students, but he felt it himself as well.
Jon Duke, MD, MS, an OHDSI veteran who collaborated on the LEGEND hypertension study published recently in Lancet, is Director of Health Informatics at Georgia Tech, home of the largest computer science graduate program in the nation. When he took over the Intro to Health Informatics course in 2018, he decided to introduce population-level analytics to a rising generation of data scientists.
EHDEN Knee Replacement Study Results Published In Lancet Rheumatology; OHDSI Tools, Collaborators Helped Lead Important Study
 The IMI European Health Data & Evidence Network (EHDEN) project is pleased to announce the publication of the results of its first ‘study-a-thon’ in Lancet Rheumatology the effectiveness and safety associated with unicompartmental versus total knee replacement, a milestone after its first year.1
The IMI European Health Data & Evidence Network (EHDEN) project is pleased to announce the publication of the results of its first ‘study-a-thon’ in Lancet Rheumatology the effectiveness and safety associated with unicompartmental versus total knee replacement, a milestone after its first year.1
The choice of which type of knee replacement to recommend remains difficult for surgeons, and there remains insufficient information to inform them and patients of the best approach, dependent on the patient’s personal context.
Researchers associated with the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) network and EHDEN met in Oxford for five days in December 2018 to design, analyze and draft a report of the study results. The resulting study emulated to the extent possible, the design of the five year Total or Partial Knee Arthroplasty Trial (TOPKAT). The study-a-thon assessed whether the efficacy results seen in the trial translated into effectiveness in real-world settings and provided further consideration of safety outcomes that were too uncommon to assess in TOPKAT.
Lancet Paper Shows Most Popular Hypertension Drug Isn’t Most Effective, Per OHDSI’s LEGEND Study
Thiazide diuretics demonstrate better effectiveness and cause fewer side effects than ACE inhibitors as first-line antihypertensive drugs, according to a report published Oct. 24 in The Lancet. The study factors insurance claim data and electronic health records from 4.9 million patients across nine observational databases, making it the most comprehensive one ever on first-line antihypertensives, and it provides additional context to the 2017 guidelines for high blood pressure treatment developed by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and American Heart Association (AHA).
Collaborators in the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) network produced the paper “Comprehensive comparative effectiveness and safety of first-line antihypertensive drug classes: a systematic, multinational, large-scale analysis” as part of the collaborative’s ongoing Large-Scale Evidence Generation and Evaluation across a Network of Databases (LEGEND) project, which applies high-level analytics to perform observational research on hundreds of millions of patient records within OHDSI’s international database network.
OHDSI researchers believe LEGEND will continue to significantly enhance how real-world evidence is used to study important healthcare questions that impact millions of patients worldwide.
Symposium Research Will Be Virtually Unveiled During #OHDSISocialShowcase
 There were more than 80 research highlights presented during the Collaborator Showcase at the 2019 OHDSI U.S. Symposium. For those who couldn’t attend, or who want to check out all the OHDSI innovations over the last year, you’ll have your chance on the OHDSI Twitter and LinkedIn platforms. Each weekday, a different poster will be highlighted with an individual URL. You’ll be able to check out the poster, as well as other materials the author may have included (abstract, software demo, lightning talk, etc.).
There were more than 80 research highlights presented during the Collaborator Showcase at the 2019 OHDSI U.S. Symposium. For those who couldn’t attend, or who want to check out all the OHDSI innovations over the last year, you’ll have your chance on the OHDSI Twitter and LinkedIn platforms. Each weekday, a different poster will be highlighted with an individual URL. You’ll be able to check out the poster, as well as other materials the author may have included (abstract, software demo, lightning talk, etc.).
Book of OHDSI Introduced At Symposium As Central Respository For Current, Potential Collaborators
 Martijn Schuemie, PhD, took the stage at the 2019 OHDSI U.S. Symposium and laid out a collection of internet locations where potential collaborators could learn about the tools and best practices developed within the community. To an audience that included about 200 first-time attendees, it must have been a daunting moment.
Martijn Schuemie, PhD, took the stage at the 2019 OHDSI U.S. Symposium and laid out a collection of internet locations where potential collaborators could learn about the tools and best practices developed within the community. To an audience that included about 200 first-time attendees, it must have been a daunting moment.
That feeling wouldn’t last long, as Schuemie followed by reaching under a white cover and pulling out the first version of the Book of OHDSI, the product of a year-long collaborative effort within the community to provide the best documentation for all aspects of OHDSI. Twenty chapters within five sections (the OHDSI Community, Uniform Data Representation, Data Analytics, Evidence Quality, and OHDSI Studies) were written to empower any new researcher with the ability to generate real-world evidence to improve the healthcare community.
For those who didn’t attend the Symposium, the Book of OHDSI is available here as HTML, as well as EPUB and PDF (click the small download icon at the top). Anybody who wants an actual copy of the book can order it through Amazon at cost price.
 Check Out Our All-Encompassing 2019 Symposium Recap Page!
Check Out Our All-Encompassing 2019 Symposium Recap Page!
The fifth annual OHDSI Symposium was a tremendous success. From the insightful talks and impressive poster presentations on Monday to the spectacular Women in Real-World Analytics Leadership Forum and the six tutorials, there is no shortage of important material that is now available from this event (including videos of all speeches and tutorials, as well as slides from the presentations). The page also includes video and photo recaps from the weekend, as well as the virtual collaborator showcase, which highlights more than 80 posters and software demos from the event.
A Look Inside What Is Coming at the 2019 OHDSI Symposium
Using real-world evidence to meaningfully impact the healthcare community will be the prevailing theme Sept. 15-17 during the 5th annual OHDSI U.S. Symposium. Collaborators from around the world will discuss both the direction of the OHDSI community, as well as some of its most important research achievements of the past year, in the highlight event on the OHDSI calendar.
The symposium takes place at the Bethesda North Marriott Hotel & Conference Center, and for the first time, it will include a Women in Real-World Analytics Leadership Forum, hosted Sunday night by the Women of OHDSI. This free event, which is open to all symposium attendees (you can RSVP here), will feature four prominent leaders in the real-world analytics community (Noémie Elhadad, Violanda Grigorescu, Janet Woodcock, and Joanne Waldstreicher), each of whom will share thoughts on their own journey, where they see this emerging discipline headed, and how OHDSI collaborators can improve healthcare in the future.

OHDSI FYI: How To Start A New Working Group
There has been interest recently in developing new working groups within the OHDSI community, but many have wondered what it takes to actually start a new working group. This was addressed previously in an OHDSI forum post, but we wanted to share the steps with you again.
An OHDSI working group represents a group of OHDSI collaborators who hold regular meetings with the purpose of developing shared solutions to tackle a common problem or address a knowledge/technology gap. A group of collaborators aiming to complete a network research study can be considered a study working group and are encouraged to follow these guidelines.
PheValuator Paper Highlights Potential For Reliable Phenotype Evaluation In Future Research
 Constructing phenotype algorithms (PAs) is a primary method for both defining diseases and identifying subjects at risk for disease in observational research. While the role of PAs is crucial for effective, reproducible research, the ability to complete detailed PA evaluations has traditionally been limited due to both cost and efficiency.
Constructing phenotype algorithms (PAs) is a primary method for both defining diseases and identifying subjects at risk for disease in observational research. While the role of PAs is crucial for effective, reproducible research, the ability to complete detailed PA evaluations has traditionally been limited due to both cost and efficiency.
Lead author Joel Swerdel provided a potential solution to this challenge in PheValuator: Development and evaluation of a phenotype algorithm evaluator, published in the latest issue of the Journal of Biomedical Informatics. Utilizing tools within the OHDSI Network, the research team developed a method that showed promise for reliable phenotype evaluation without reliance on manual review of patient data.
Phenotype Sharing Feasibility Through OMOP Demonstrated In Recent JBI Paper
 Traditional methods of identifying phenotypes over varied networks of electronic health record (EHR) databases is challenging. The recently published “Facilitating Phenotype Transfer Using A Common Data Model” paper in the Journal of Biomedical Informatics demonstrated success in creating a systematic process for sharing disease definitions—known as phenotypes—across a network using the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) OMOP Common Data Model, which could lead to dramatic improvements in the ability to study diseases in the future.
Traditional methods of identifying phenotypes over varied networks of electronic health record (EHR) databases is challenging. The recently published “Facilitating Phenotype Transfer Using A Common Data Model” paper in the Journal of Biomedical Informatics demonstrated success in creating a systematic process for sharing disease definitions—known as phenotypes—across a network using the Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics (OHDSI) OMOP Common Data Model, which could lead to dramatic improvements in the ability to study diseases in the future.
George Hripcsak, MD, MS, the co-PI of the OHDSI Coordinating Center at Columbia University, served as lead author for a paper that demonstrated an efficient alternative to phenotype sharing that allows for rapid exchange and execution across different medical centers, improving the speed and reproducibility of the research process.
China Symposium, Tutorials Welcome Potential Collaborators To OHDSI Community

The 2019 China Symposium introduced top scholars, practioners, researchers and more to the potential of OHDSI collaboration.
The annual OHDSI China Symposium, which took place June 27-29 at Shanghai Jiaotong University, reinforced the impressive potential of the OHDSI network via the collaboration of multiple, motivated stakeholders.
Attendees of the symposium included experts and scholars from major universities in China, medical information-related practitioners of various medical and health institutions, medical-related scientific research personnel, and workers interested in big data in the pharmaceutical industry.
The symposium led off with a pair of keynote addresses, including one entitled “FEEDERNET: Evolution of Distributed Research Network in Korea” by OHDSI collaborator Rae Woong Park. Park is a top advocate for the development of OHDSI in Korea, and his presentation helped demonstrate the unique possibilities of the network.
OHDSI Provides Oxford Tutorial, Leads One-Day Study That Posts Impressive Results

OHDSI collaborated with the Oxford Summer School session for a tutorial on tools and a one-day study.
The boundless potential to create real-world evidence through OHDSI was demonstrated for a second time in as many weeks, as collaborators from both sides of the Atlantic met in England during the Real World Epidemiology: Oxford Summer School session.
Peter Rijnbeek and Patrick Ryan led the June 27 session on the OMOP common data model, OHDSI, and the analytical use case of patient-level prediction.
Rijnbeek and Ryan supported the mission of OHDSI collaborator and Oxford professor Dani Prieto-Alhambra. The previous week, Rijnbeek and Ryan supported OHDSI collaborators Iannis Drakos and Ismail Gögenur during a three-day seminar for the Denmark Center for Surgical Sciences (CSS).
“It was great to have OHDSI join our summer school,” Prieto-Alhambra said. “Forty people’s jaws dropped whilst learning what can be achieved through open science, community and a common data model!”